User's Guide and Reference
The boundary of a multipolygon is the cumulative length of its
element's exterior and interior rings. The interior of a
multipolygon is defined as the cumulative interiors of its element
polygons. The boundary of a multipolygon's elements can intersect
only at a tangent point. In addition to the other properties inherited
from the superclass geometry, multipolygons have area. Multipolygons
define features such as a forest stratum or a non-contiguous parcel of land
such as an island chain.
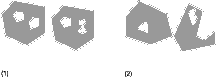
Figure 13. Multipolygons.
- A multipolygon with two polygon elements. The boundary is defined by the two exterior rings and the three interior rings.
- A multipolygon with two polygon elements. The boundary is defined by the two exterior rings and the two interior rings. The two polygon elements intersect at a tangent point.
Functions that operate on multipolygons:
-
ST_Area
- Takes a multipolygon and returns the cumulative area of its polygon
elements as a double precision number. For more information, see ST_Area.
-
ST_Centroid
- Takes a multipolygon and returns a point that is its geometric-weighted
center. For more information, see ST_Centroid.
- ST_NumGeometries
- Takes a homogeneous collection and returns the number of base geometry
elements it contains. For more information, see ST_NumGeometries.
- ST_GeometryN
- Takes a homogeneous collection and an index and returns the nth base
geometry. For more information, see ST_GeometryN.
[ Top of Page | Previous Page | Next Page ]