This example shows a typical request flow through Mobile Portal Accelerator.
Figure 1. Example IBM® Mobile Portal Accelerator flow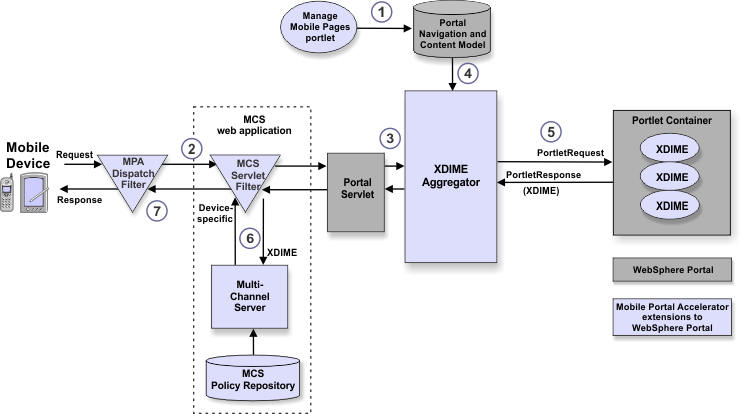

- Portal administrators use the Manage Mobile Pages portlet to define the navigation for a mobile portal. The defined navigation hierarchy defines nodes (pages, URLs, and portlets) and the optional extended properties specifying device capability, type, and display requirements for each node. These nodes and properties are stored in the WebSphere® Portal mobile database.
- When the WebSphere Portal server receives a request, the MPADispatchFilter forwards this request to the MCS web application. If the request is from a mobile device, the MCS web application prepares the request for processing and forwards it back to the Portal servlet. If the request is from a PC device, the MCS web application forwards the request as-is back to Portal servlet.
- The Portal servlet uses the supported clients table to determine which portal theme (aggregator) should handle the request. Mobile device requests are directed to the XDIME theme by the supported clients table.
- The XDIME aggregator queries the Portal Model to determine the navigation and portlet availability based on the user and extended properties of each node. If the request is for a portlet node, the request is passed to the portlet.
- If the portlet is an XDIME portlet, the portlet renders the content in XDIME and returns the content to the XDIME aggregator.
- The aggregated XDIME page is sent to the MCS web application. MCS transforms the XDIME content for the page to device-specific markup by using the appropriate policies in the MCS policy repository.
- The MCS web application returns the device-specific content for delivery to the MPADispatchFilter, which in turn delivers this markup to the mobile device.