icon.
| Note: | You should be connected to the Sample Basic database. If you are not connected, follow the steps in Connecting to a Database. |
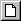
Figure 70. Initial Worksheet for Member Selection
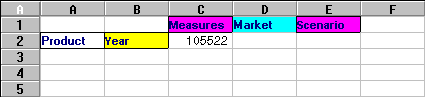 |
Hyperion Essbase displays the Essbase Member Selection dialog box. In the Essbase Member Selection dialog box, Hyperion Essbase displays the Product dimension in the Dimension list box and its children, Colas, Root Beer, Cream Soda, Fruit Soda, and Diet Drinks, in the Members list box.
Figure 71. Essbase Member Selection Dialog Box
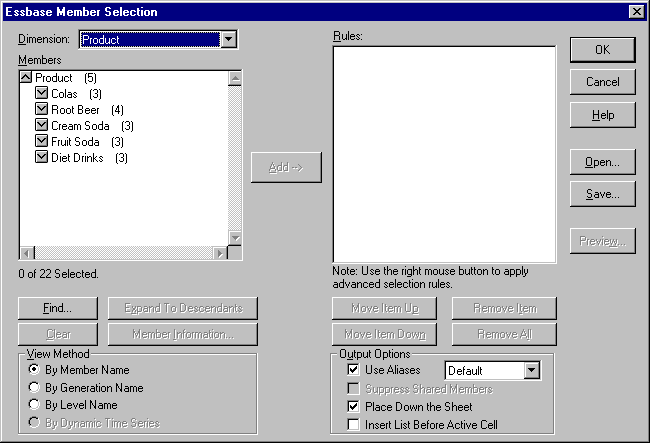 |
Hyperion Essbase displays the Member Information dialog box. The dialog box provides information about the selected member, such as dimension, generation, level, storage setting, formula, UDAs, and member comments.
Figure 72. Member Information Dialog Box
 |
| Note: | Alternatively, you can double-click an item in the Members list box to add the item. |
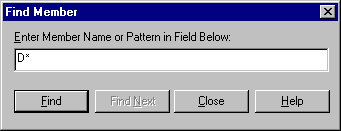
Hyperion Essbase displays the Find Member dialog box.
In the Find Member dialog box, you can do pattern-match searches for members in the selected dimension. You can use Wildcard patterns--(trailing asterisk, *) and (single-character match, ?). Hyperion Essbase locates the members that match the text string (in alphabetical order) and keeps them selected so that they can be selected as a group.
| Note: | You can use the trailing asterisk wildcard and single-character wildcard in the text string. The * wildcard replaces a string of characters, whereas the ? wildcard replaces a single character. J?n and 100* are examples of valid wildcard strings; *-10 and J*n are examples of invalid wildcard strings. |
Figure 73. Find Member Dialog Box
 |
Hyperion Essbase locates and selects Diet Cream. Its parent, Cream Soda, is also selected because it was highlighted before the search.
Hyperion Essbase displays All Children and Member next to Colas in the Selection Rules list box.
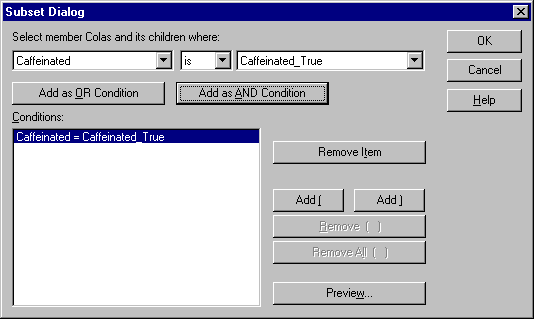
Hyperion Essbase displays the Subset Dialog box, where you can further define conditions for the selected member.
| Note: | You can define a maximum of 50 conditions in the Subset Dialog box. |
Hyperion Essbase displays Caffeinated = Caffeinated_True in the Conditions list box.
When you use Add as AND Condition, the subsetting condition in the Conditions list box is evaluated using AND logic. AND logic means that the selection must meet the current condition and the following condition in the Conditions list box.
Figure 74. Subset Dialog Box (Before Adding Conditions)
 |
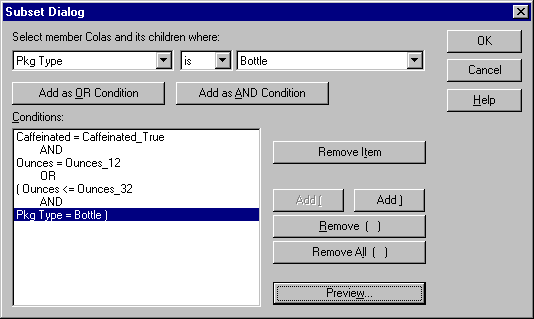
Hyperion Essbase displays Ounces = Ounces_12 in the Conditions box.
Hyperion Essbase displays Ounces <= Ounces_32 in the Conditions box.
When you use the Add as OR Condition, the subsetting condition in the Conditions list box is evaluated using OR logic. OR logic means that the selection must meet the current condition or the following condition in the Conditions list box.
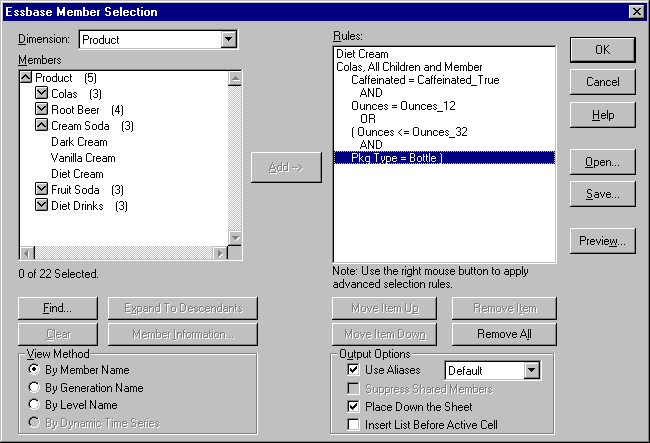
Hyperion Essbase displays Pkg Type = Bottle in the Conditions list box.
The Add ( and Add ) buttons add a left parenthesis and right parenthesis, respectively, to selected items. Use parentheses for grouping multiple subsetting conditions to determine the order of priority for analyzing the conditions. Each item in the Conditions list box can have either the left or right parenthesis, but not both. In this example, Hyperion Essbase first evaluates members that are equal to or less than 32 ounces and are packaged in a bottle. Hyperion Essbase then evaluates the results from this condition against members that are 12 ounces.
| Note: | Use the Remove ( ) button to remove an individual group of parentheses from a selected item in the Conditions list box. Use the Remove All ( )button to remove all parenthetical groupings from the Conditions list box. |
The Subset Dialog box is displayed as follows:
Figure 75. Subset Dialog Box (After Adding Conditions)
 |
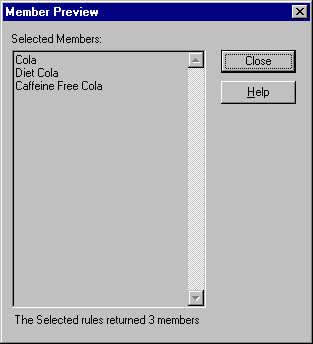
In the Member Preview dialog box, you can view the member selection that results from the conditions you defined.
Figure 76. Member Selection That Results from Subsetting Conditions
 |
The conditions you set in the Subset dialog box are displayed in the Selection Rules list box.
Each time you click the Move Item Up or Move Item Down button, the selected item and its associated subset conditions move up or down one position in the Selection Rules list box. You can move only the top-level item (the item you added from the Members list box), not the individual subset conditions.
Figure 77. Selecting Members Completed
 |
Hyperion Essbase displays the Member Preview dialog box.
Figure 78. Members to be Retrieved in Worksheet
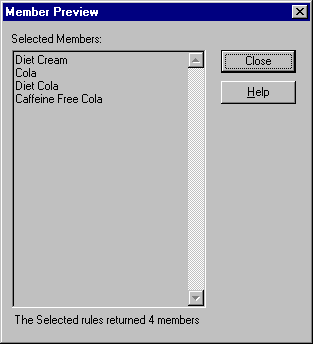 |
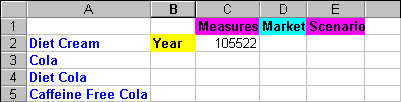
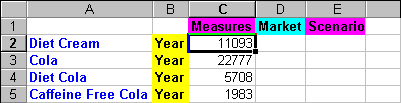
Figure 79. Result of Selecting Members
 |
| Note: | The FlashBack command cannot undo a Member Selection action. |
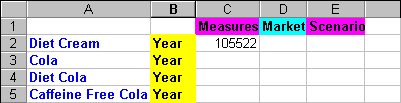
You need to do this step so that every product has a matching Year dimension associated with it in the report.
Figure 80. Worksheet After Adding the Year Dimension to All States
 |
Hyperion Essbase retrieves data for the members that you selected and also applies the styles you previously set.
Figure 81. Result After Retrieving with Member Selection
 |