This chapter describes the relational database tables that are used for replication.
Table 34, Table 35, and Table 36 provide brief descriptions of the tables listed in this chapter. When you become familiar with the tables, you can use Figure 23 and Figure 24 as a quick reference for the source and control server tables, table keys, and their parameters.
Important: You must not use SQL to update some of the control tables (see particular table descriptions for details). Altering control tables inappropriately can cause problems such as unexpected results, loss of data, and reduced replication performance.
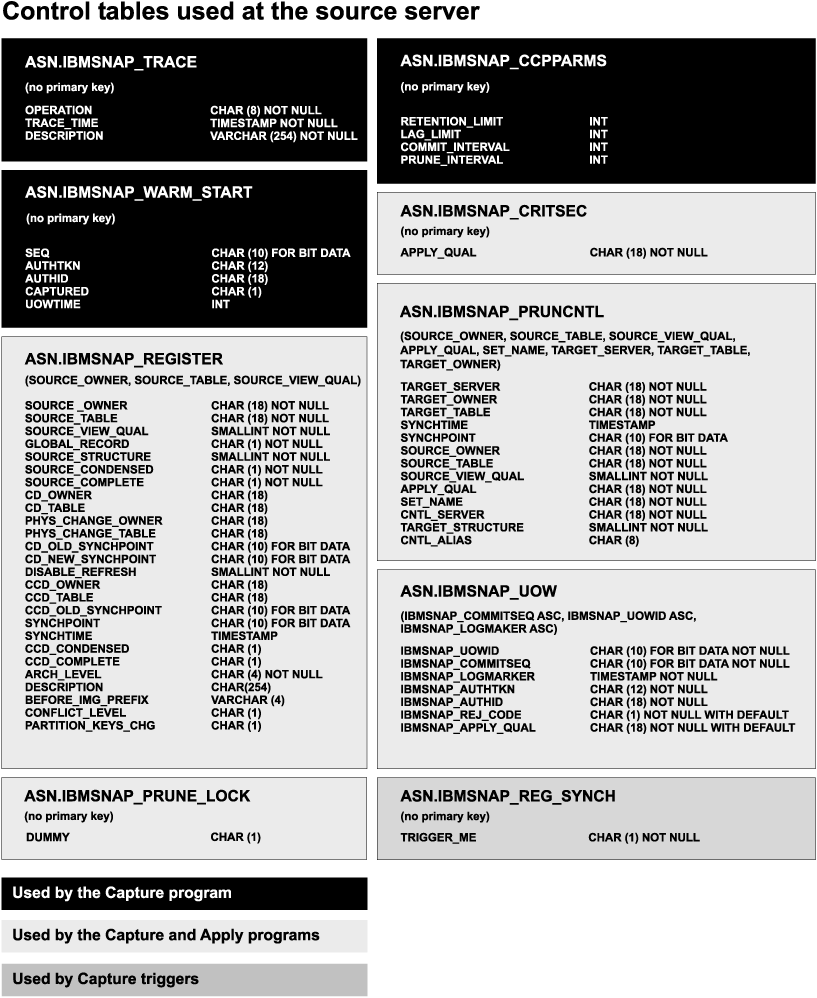
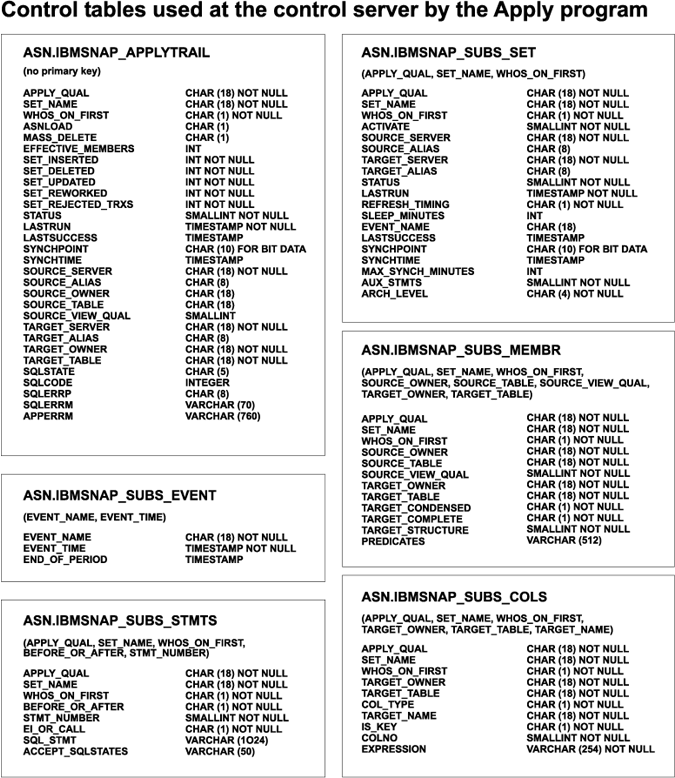
Figure 23 and Figure 24 show the tables at the source and control servers, table keys, and their parameters.
Figure 23. Tables used at the source server. The tables used by the Capture program, Apply program, and Capture triggers at the source server.
 |
Figure 24. Tables used at the control server. The tables used by the Apply program at the control server.
 |
The following table provides a list of tables used at the source server
during DB2 replication.
Table 34. Quick reference for tables used at the source server
| Table name | Internal name and description | See topic |
|---|---|---|
| Apply-qualifier-cross-reference table (AS/400 specific) | ASN.IBMSNAP_AUTHTKN
Contains information to support update-anywhere. | "Apply-qualifier-cross-reference table (AS/400 specific)" |
| Capture enqueue table
(VM and VSE specific) | ASN.IBMSNAP_CCPENQ
Used to ensure that only one Capture program is running per database. | "Capture enqueue table (VM and VSE specific)" |
| Change data table | CD
A table that contains changed data information. Created when a replication source is defined. | "Change data table" |
| Consistent-change-data table | userid.target_table
Contains additional columns to help identify transactions. This table stores the individual operations, transactions, and the approximate times of those transactions. | "Consistent-change-data table" |
| Critical section table | ASN.IBMSNAP_CRITSEC
Used to prevent circular replication for update-anywhere replication. | "Critical section table" |
| Pruning control table | ASN.IBMSNAP_PRUNCNTL
Coordinates synchpoint updates by allowing the Apply program to communicate with the Capture program and coordinates pruning of tables. There is one pruning control table at each source server and one row per source-to-target copy. | "Pruning control table" |
| Prune lock table | ASN.IBMSNAP_PRUNE_LOCK
Used to serialize the access of staging tables during a cold start or retention limit pruning. | "Prune lock table" |
| Register table | ASN.IBMSNAP_REGISTER
Contains information about replication sources, such as the names of the replication source tables, their attributes, and their corresponding CD and CCD table names. | "Register table" |
| Register extension table (AS/400 specific) | ASN.IBMSNAP_REG_EXT
An extension of the register table. Contains additional information about replication sources, such as the journal name and the remote source table's database entry name. | "Register extension table for AS/400" |
| Register synchronization table | ASN.IBMSNAP_REG_SYNCH
When replicating from a non-IBM data source, an update trigger on this table initiates an update of the SYNCHPOINT value for all the rows in the register table before the Apply program reads the information from the register table. | "Register synchronization table" |
| Trace table | ASN.IBMSNAP_TRACE
Contains Capture program audit trail information. | "Trace table" |
| Tuning parameters table | ASN.IBMSNAP_CCPPARMS
Contains parameters that you can modify to control the performance of the Capture program. | "Tuning parameters table" |
| Unit-of-work table | ASN.IBMSNAP_UOW
Contains information about committed transactions. Used to maintain transaction consistency. | "Unit-of-work table" |
| Warm start table | ASN.IBMSNAP_WARM_START
Contains information that enables the Capture program to resume capturing from the point in the log or journal where it last stopped. For AS/400 platforms, this table is used to determine the starting time of the RCVJRNE (Receive Journal Entry) command. | "Warm start table" |
The following table provides a list of tables used at the control
server during DB2 replication.
Table 35. Quick reference for tables used at the control server
| Table name | Internal name and description | See topic |
|---|---|---|
| Apply trail table | ASN.IBMSNAP_APPLYTRAIL
Contains Apply program audit trail and problem diagnostic information. | "Apply trail table" |
| Subscription columns table | ASN.IBMSNAP_SUBS_COLS
Maps target table or view columns to the corresponding source table or view column or user-defined expression. | "Subscription columns table" |
| Subscription events table | ASN.IBMSNAP_SUBS_EVENT
Contains user-defined event names that control the execution of a subscription set. You modify this table using SQL. | "Subscription events table" |
| Subscription set table | ASN.IBMSNAP_SUBS_SET
Contains processing information for a set of subscription-set members, which are processed by the Apply program as a group. | "Subscription set table" |
| Subscription statements table | ASN.IBMSNAP_SUBS_STMTS
Contains SQL statements or stored procedure calls that are defined in a subscription set. | "Subscription statements table" |
| Subscription-targets-member table | ASN.IBMSNAP_SUBS_MEMBR
Identifies a source and target table (or view) pair and specifies processing information for that pair. | "Subscription-targets-member table" |
| Row-replica-target-list table
(Microsoft Jet specific) | ASN.IBMSNAP_SUBS_TGTS
Maintains the names of the row-replica tables. Row-replica tables are a type of target table used specifically with the Microsoft Jet database. | "Row-replica-target-list table (Microsoft Jet specific)" |
| Subscription-schema-changes table
(Microsoft Jet specific) | ASN.IBMSNAP_SCHEMA_CHG
Used to signal add or delete modifications to a subscription. | "Subscription-schema-changes table (Microsoft Jet specific)" |
The following table provides a list of tables used at the target
server.
Table 36. Quick reference for target tables
| Table name | Internal name and description | See topic |
|---|---|---|
| Base aggregate table | userid.target_table.target_table
Contains data aggregated from a source table. | "Base aggregate table" |
| Change aggregate table | userid.target_table
Contains data aggregations based on changes from a source table. | "Change aggregate table" |
| Consistent-change-data table | userid.target_table
Contains additional columns to help identify transactions. This table stores the individual operations, transactions, and the approximate times of those transactions. | "Consistent-change-data table" |
| Point-in-time table | userid.target_table
Identical to a user copy table, except that the IBMSNAP_LOGMARKER column is included to record a specific commit time from the source server. | "Point-in-time table" |
| Replica table | userid.target_table
A type of target table used for update-anywhere replication. | "Replica table" |
| Row-replica table
(Microsoft Jet specific) | userid.target_table
A type of Microsoft Jet target table that can be updated. | "Row-replica table (Microsoft Jet specific)" |
| User copy table | userid.target_table
A copy of the user table. | "User copy table" |
| Conflict table
(Microsoft Jet specific) | IBMSNAP_target_name_CONFLICT
Contains row data for DataPropagator for Microsoft Jet-detected conflict losers. | "Conflict table (Microsoft Jet specific)" |
| Error information table
(Microsoft Jet specific) | IBMSNAP_ERROR_INFO
Contains additional information to identify the row-replica table and row that caused an error. | "Error information table (Microsoft Jet specific)" |
| Error messages table
(Microsoft Jet specific) | IBMSNAP_ERROR_MESSAGE
Contains error codes and error messages. There can be more than one row in this table. Depending on the error code, additional information will be available in the error information, error-side-information, and conflict tables. | "Error messages table (Microsoft Jet specific)" |
| Error-side-information table
(Microsoft Jet specific) | IBMSNAP_SIDE_INFO
Contains the names of the conflict tables. | "Error-side-information table (Microsoft Jet specific)" |
| Key string table
(Microsoft Jet specific) | IBMSNAP_GUID_KEY
Maps the Microsoft Jet table identifiers and row identifiers to primary key values when the following actions occur:
| "Key string table (Microsoft Jet specific)" |
| Synchronization generations table
(Microsoft Jet specific) | IBMSNAP_S_GENERATION
Prevents cyclic updates from propagating back to the RDBMS from a Microsoft Jet database. | "Synchronization generations table (Microsoft Jet specific)" |
This section describes the tables used at the source server and the columns in each table. These tables are created automatically the first time that you define a replication source if you use the Control Center and if they do not already exist on the source server. On the AS/400 platform, these tables are created automatically in the following situations if they do not exist already on the source server:
The administration tools use the information in the register, register extension, and pruning control tables to define your source and target tables for replication. After you define your replication sources, the Capture program uses the tuning parameters, capture enqueue, warm start, critical section, trace, and Apply-qualifier-cross-reference tables to control and audit your data. In addition to all the Capture program control and audit tables mentioned, the Capture triggers also use the register synchronization table to control data. The UOW and CD tables track data that has not yet been replicated.
This table contains information that you can update by using SQL.
ASN.IBMSNAP_REGISTER
The register table contains information about replication sources, such as the names of the replication source tables, their attributes, and their staging table names. A row is automatically inserted into this table every time a new replication source is defined at this server. You must update this table to maintain an external CCD table.
The register table is the place to look if you need to know how you defined your replication sources.
Table 37 provides a brief description of the columns in the register
table.
Table 37. Columns in the register table
Important: Do not use SQL to update this table. Altering this table inappropriately can cause unexpected results and loss of data.
ASN.IBMSNAP_REG_EXT
This table is an AS/400-specific table that provides supplemental information for the register table, ASN.IBMSNAP_REGISTER. For every register table row, there is a matching row in the register extension table containing a few additional AS/400-specific columns.
This table is maintained by a trigger program (program QZSNJRNL in library QDPR) on the register table (ASN.IBMSNAP_REGISTER). The trigger is defined at the time the register table is created.
Use this table to complete the information from the register table to track where and how you defined your replication sources on an AS/400 server.
Table 38 provides a brief description of the columns in the register
extension table.
Table 38. Columns in the register extension table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| SOURCE_OWNER | The owner of the source table or view. |
| SOURCE_TABLE | The source from which data is being captured. |
| SOURCE_NAME | A 10-character source table (or view) system name, used to issue commands. |
| SOURCE_MBR | The name of the source table member being captured. Used for issuing Receive Journal Entry (RCVJRNE) commands and ALIAS support. |
| SOURCE_TABLE_RDB | When using remote journals, this column contains the database name of the system where the source table actually resides. For non-remote-journal cases, this column is NULL. |
| JRN_LIB | The library name of the journal that the source table uses. |
| JRN_NAME | The name of the journal used by a source table. An asterisk followed by nine blanks in this column means that the source table is not currently in a journal. Therefore, it is not possible to capture data for this source table. |
| FR_START_TIME | Time at which the full refresh starts. This column is updated by Capture for AS/400, not the administration tool, during operations. |
| SOURCE_VIEW_QUAL | Supports the view of subscriptions by matching the similar column in the register table. This value is set to equal 0 for physical tables that are defined as a source and is greater than 0 for views that are defined as sources. You must have this column to support multiple subscriptions for different source views with identical SOURCE_OWNER and SOURCE_TABLE column values. |
Important: Do not use SQL to update this table. Altering this table inappropriately can cause unexpected results and loss of data.
ASN.IBMSNAP_PRUNCNTL
The pruning control table coordinates the pruning of the change data (CD) tables, which have the potential for unlimited growth. For each new subscription set, the Apply program first updates the pruning control table and then it begins a full refresh of every member of the new subscription set. After the full refresh, the Capture program begins capturing changes from the replication source. When the Capture program begins to capture data, it updates the pruning control table to notify the Apply program. During each Apply cycle, the Apply program updates the pruning control table to indicate the last change applied. The Capture program then uses the information to prune the CD and UOW tables.
The rows in the pruning control table are not deleted during a cold start of the Capture program. The administration tools use the values from the pruning control table to provide a list of copies defined as source tables and views.
There is one pruning control table at each source server and one row in the pruning control table for each subscription-set member.
You can manually prune your table by issuing the prune command or have it done automatically by updating the PRUNE_INTERVAL column in the tuning parameters table. See Tuning parameters table for more information about using the tuning parameters table.
Use this table to monitor the pruning status of your CD and UOW tables.
Table 39 provides a brief description of each of the columns in the
pruning control table.
Table 39. Columns in the pruning control table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| TARGET_SERVER | The database name of the server where target tables or views are stored. |
| TARGET_OWNER | A qualifier for a target table or view. |
| TARGET_TABLE | The target to which data is being applied. |
| SYNCHTIME | A source server timestamp. The SYNCHTIME value equals the
SYNCHTIME field value in the subscription set table. The Capture
program or an external program, such as IMS DataPropagator, updates this
timestamp whether there are changes to be processed or not.
The Apply program uses this value when advanced conflict detection is selected for update-anywhere replication to ensure that the Capture program captures all outstanding changes for a replication source table. |
| SYNCHPOINT | The SYNCHPOINT value equals the SYNCHPOINT field value in the subscription set table. This value is used to coordinate the pruning of CD tables. The Apply program sets this initial value to hex 0, indicating refresh. If the Apply program sets a nonzero value, the CD table can be eligible for pruning. |
| SOURCE_OWNER | The owner of the source table or view. |
| SOURCE_TABLE | The source from which data is being captured. |
| SOURCE_VIEW_QUAL | Supports the view of physical tables by matching the similar column in the register table. This value is set to 0 for physical tables that are defined as sources and is greater than 0 for views that are defined as sources. This column is used to support multiple subscriptions for different source views with identical SOURCE_OWNER and SOURCE_TABLE column values. |
| APPLY_QUAL | A unique identifier for a group of subscription sets. This case sensitive value is supplied by the user when defining a subscription set. This column is part of the foreign key from the subscription set table. See Subscription set table for more details. |
| SET_NAME | An identifier for a group of subscription-set members. This value is supplied when you define a subscription set. This column is part of the foreign key from the subscription set table. See Subscription set table for more details. |
| CNTL_SERVER | The database name of the control server for the Apply program updating this row. |
| TARGET_STRUCTURE | A value that identifies the type of target table or view:
|
| CNTL_ALIAS | The DB2 Universal Database alias corresponding to the control server named in the CNTL_SERVER column. |
This table contains information that you can update by using SQL.
ASN.IBMSNAP_CCPPARMS
This table contains parameters that you can modify to control the performance of the Capture program. You can set these parameters to modify the length of time that you retain data in the CD table, the amount of time that the Capture program is allowed to lag in processing log records, how often data will be committed, and how often your CD and UOW tables are pruned. These modifications must be done manually because there are no DB2 DataPropagator processes that update this table after it is created. The Capture program can read your modifications only during its start processing; therefore, you should stop and start the Capture program if you want your modifications to take effect.
Table 40 provides a brief description of the columns in the tuning
parameters table.
Table 40. Columns in the tuning parameters table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| RETENTION_LIMIT | The age limit, in minutes, for keeping CD table rows. This value is used with the SYNCHPOINT column of the pruning control table to determine the pruning limit. Any change data rows older than this value are pruned, even if they have not been copied to all targets. Transactions rejected after update conflict detection will have their changes pruned by RETENTION_LIMIT aging, not by normal pruning. The default value is 10 080 minutes (which equals seven days). |
| LAG_LIMIT | The amount of time, in minutes, that the Capture program is allowed to lag in processing log records before it shuts itself down. During periods of high update frequency, full refreshes can be more economical than updates. The default value is 10 080 (which equals seven days). |
| COMMIT_INTERVAL | The Capture program commit threshold, in seconds, for any inserts,
updates, or deletes to the global UOW table and any pruning control
tables. The default value is 30.
On systems that do not support ISOLATION (UR), this value should be less than the DB2 lock timeout value to prevent Apply program instances from timing out due to contention with the Capture program. |
| PRUNE_INTERVAL | The Capture program commit threshold, in seconds, for automatic or manual pruning of CD and UOW rows that are no longer needed. The default value is 300. Values set lower save space, but increase processing costs. Values set higher require more CD and UOW table space, but decrease processing costs. There is no effect on table space or processing cost when the NOPRUNE option is selected. |
Important: Do not use SQL to update this table. Altering this table inappropriately can cause unexpected results and loss of data.
ASN.IBMSNAP_CCPENQ
The Capture enqueue table is used in the VM and VSE environments only. This table is used to ensure that there is only one Capture program running per database.
Table 41 provides a list and a brief description of the Capture
enqueue table column.
Table 41. Capture enqueue table column
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| LOCKNAME | Unique name of the resource for this database. |
Important: Do not use SQL to update this table. Altering this table inappropriately can cause unexpected results and loss of data. If you delete all the rows from this table, the Capture program will take longer to start because it must calculate a restart position based on the contents of the CD tables, the UOW table, and the control tables.
ASN.IBMSNAP_WARM_START
This table is created in the same database as the register table and contains information that enables the Capture program to restart from the last log or journal record read. Use the information in this table to avoid a full refresh of your system.
You do not have to recover this table if it is damaged. Simply create an empty table before warm starting the Capture program.
The following three tables show platform-specific layouts of the warm start table:
Table 42. Columns in the warm start table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| SEQ | The last captured sequence number from the log or journal record. Used for quickly restarting following a shutdown or failure. |
| AUTHTKN | The DB2 token for the unit of work associated with the SEQ log or journal record. AUTHTKN length is 12 characters. If you supply a longer value, it is truncated. |
| AUTHID | The DB2 authorization ID for the unit of work associated with the SEQ log or journal record. AUTHID length is 18 characters. If you supply a longer value, it is truncated. |
| CAPTURED | A flag indicating whether or not this unit of work was captured.
|
| UOWTIME | The MVS clock, or Windows NT, HP-UX, Sun Solaris, OS/2, and AIX Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) clock indicating when the unit of work associated with the SEQ position was captured (source server timestamp). |
Table 43. Columns in the warm start table for VM and VSE platforms
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| SEQ | The last captured sequence number from the log or journal record. Used for quickly restarting following a shutdown or failure. |
| UOWID | The unit-of-recovery ID from the log record header for this unit of work. |
| AUTHID | The DB2 authorization ID for the unit of work associated with the SEQ log or journal record. |
| CAPTURED | A flag indicating whether or not this unit of work was captured.
|
| UOWTIME | The VSE and VM time-of-day clock indicating when the unit of work associated with the SEQ log or journal record was captured (source server timestamp). |
For AS/400, the warm start table is used to determine the starting time of the RCVJRNE (Receive Journal Entry) command. A row is inserted into the warm start table for each journal that is used by a replication source or a group of replication sources.
Table 44 provides a brief description of the columns in the warm
start table for the AS/400 platform.
Table 44. Columns in the warm start table for AS/400 platform
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| JRN_LIB | The library name of the journal. |
| JRN_NAME | The name of the journal used by a source table. An asterisk followed by nine blanks in this column means that the source table is not currently in a journal. Therefore, it is not possible to capture data for this source table. |
| JRN_JOB_NUMBER | The job number of the current job for a particular journal. If the journal is not active, this column contains the job number of the last job that was processed. |
| LOGMARKER | The timestamp of the last processed journal entry. |
| UID | A unique number that is used as a prefix for the contents of the IBMSNAP_UOWID column located in the UOW table. |
| SEQNBR | The sequence number of the last processed journal entry. |
Important: Do not use SQL to update this table. Altering this table inappropriately can cause unexpected results and loss of data.
ASN.IBMSNAP_CRITSEC
This table is used to prevent circular replication in an update-anywhere scenario.
You do not have to recover this table if it is damaged. Simply create an empty table.
Table 45 provides a brief description of the critical section table
column.
Table 45. Critical section table column
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| APPLY_QUAL | A unique identifier for a group of subscription sets. This value is supplied by the user when defining a subscription set. Each Apply process is started with an APPLY_QUAL value. This value is used during update-anywhere replication to prevent circular propagation of the changes made by the Apply program. See Subscription set table for more details. |
ASN.IBMSNAP_PRUNE_LOCK
The prune lock table is used to serialize the access of staging tables during a cold start or retention limit pruning. (Retention limit pruning is pruning after the retention limit is reached. The default retention limit is 10 080, which equals 7 days.) There are no rows in this table. The Capture and Apply programs use this table as a logical lock to serialize their operations during these critical phases. If a prune lock table does not exist, as on DB2 UDB Version 5 servers, the critical section (ASN.IBMSNAP_CRITSEC) table is locked instead. If a prune lock table does not exist, you can create one to increase the concurrency of update-anywhere subscriptions.
You do not have to recover this table if it is damaged. Simply create an empty table.
ASN.IBMSNAP_TRACE
This table contains audit trail information for the Capture program. Everything that is done by the Capture program is recorded in this table, which makes it one of the best places to look if a problem with the Capture program occurs. If you cold start the Capture program, all of the trace table's entries are deleted, so you might want to save a copy of this table before you issue a cold start command.
The following two tables show platform-specific layouts of the trace
table. Table 46 shows the layout for all platforms other than AS/400,
and Table 47 shows the AS/400 layout.
Table 46. Columns in the trace table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| OPERATION | The type of Capture program operation, for example, initialization, capture, or error condition. |
| TRACE_TIME | The time that a row is inserted into the trace table. |
| DESCRIPTION | The message ID followed by the message text. The message can be informational or error. This column contains English-only text. See Capture and Apply messages for a detailed description of the correlating message ID in the DESCRIPTION column. |
Table 47. Columns in the trace table for AS/400
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| OPERATION | The type of Capture program operation, for example, initialization, capture, or error condition. |
| TRACE_TIME | The time that a row is inserted into the trace table. |
| JOB_NAME | The fully qualified name of the job that wrote this trace entry.
|
| JOB_STR_TIME | The starting time of the job named in the JOB_NAME column. |
| DESCRIPTION | The message ID followed by the message text. The message ID is the first 7 characters of the DESCRIPTION column. The message text starts at the 9th position of the DESCRIPTION column. Refer to Replication messages for AS/400 for information about messages. |
Important: Do not use SQL to update this table. Altering this table inappropriately can cause unexpected results and loss of data.
ASN.IBMSNAP_AUTHTKN
The Apply-qualifier-cross-reference table is used in the AS/400 environment only. This table is used during update-anywhere replication to keep track of the jobs run by a particular Apply qualifier. It is pruned by the Capture program based on the retention limit. The default retention limit is 10 080, which equals 7 days.
Table 48 provides a brief description of the columns in the
apply-qualifier-cross-reference table.
Table 48. Columns in the apply-qualifier-cross-reference table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| APPLY_QUAL | An Apply qualifier, which is a unique identifier for a group of subscription sets. You supply this value when defining a subscription set. Each Apply process is started with an Apply qualifier. This value is used during update-anywhere replication to prevent circular propagation of the changes made by the Apply program. See Subscription set table for more details. |
| IBMSNAP_AUTHTKN | The job name associated with a transaction. AUTHTKN length is 12 characters. If you supply a longer value, it is truncated. Capture for AS/400 matches this column with the name of the job that issued the transaction to determine if a transaction is issued by either the Apply program or a user application. If the names match, then Capture for AS/400 copies the value from the APPLY_QUAL column to the UOW row. If the names do not match, then Capture for AS/400 sets the APPLY_QUAL column of the UOW row to blank. This column is not automatically copied to other tables; you must select it and copy it as a user data column. |
| IBMSNAP_LOGMARKER | The approximate commit time at the source server. |
Important: Altering this table might result in wasteful pruning processing.
ASN.IBMSNAP_REG_SYNCH
There is an update trigger on this table that initiates an update of the SYNCHPOINT value for all the rows in the register table when the Apply program fetches data from a non-IBM data source.
Table 49 provides a brief description of the register synchronization
table column.
Table 49. Register synchronization table column
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| TRIGGER_ME |
|
Important: Do not use SQL to update this table. Altering this table inappropriately can cause unexpected results and loss of data.
ASN.IBMSNAP_UOW
The unit-of-work (UOW) table ensures data integrity by recording transactions that were committed at the source server. The Apply program joins the UOW and CD table based on matching IBMSNAP_UOWID values to ensure that only committed changes are being copied. The results are ordered by the log or journal record sequence number of the change in the CD table within the committed units of work. If you cold start the Capture program, all of this table's entries are deleted.
| For AS/400: | Capture for AS/400 can start data capturing for only a subset of the replication sources. Therefore, Capture for AS/400 does not delete all the rows in the UOW table if you do a partial cold start. |
The Capture program requires that there is one UOW table for each source server. The Capture program inserts one new row into this table for every log or journal record that commits changes to replication sources.
| For AS/400: | There are some user programs that do not use commitment control. In such cases, the Capture program arbitrarily inserts a new UOW row after a number of rows are written to the CD table. This artificial commitment boundary helps reduce the size of the UOW table. |
The Capture program also prunes the UOW table based on information inserted into the pruning control table by the Apply program.
| For AS/400: | The UOW table is pruned by retention limits, not by the pruning control table information. |
Table 50 provides a brief description of the columns in the UOW
table.
Table 50. Columns in the UOW table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| IBMSNAP_UOWID | The unit-of-work identifier from the log record header for this unit of work. |
| IBMSNAP_COMMITSEQ | The log record sequence number of the captured commit statement. |
| IBMSNAP_LOGMARKER | The approximate commit time at the source server. |
| IBMSNAP_AUTHTKN | The authorization token associated with the transaction. This ID is useful for database auditing. For DB2 Universal Database for OS/390, this column is the correlation ID. For DB2 Universal Database for AS/400, this column is the job name of the job that caused a transaction. This column is not automatically copied to other tables; you must select it and copy it as a user data column. This column can be selected as a user data column for a noncomplete CCD target table. |
| IBMSNAP_AUTHID | The authorization ID associated with the transaction. It is useful for database auditing. AUTHID length is 18 characters. If you supply a longer value, it is truncated. For DB2 Universal Database for OS/390, this column is the primary authorization ID. For DB2 Universal Database for AS/400, this column has the name of the user profile ID under which the application that caused the transaction ran. This column holds a 10-character ID padded with blanks. This column is not automatically copied to other tables; you must select it and copy it as a user data column. This column can be selected as a user data column for a noncomplete CCD target table. |
| IBMSNAP_REJ_CODE | This value is set only during update-anywhere replication if
conflict detection is specified as standard or advanced when you define your
replication source.
|
| IBMSNAP_APPLY_QUAL | This column prevents circular replication during update-anywhere processing. It remains blank for local updates, but contains the name of the associated Apply program for updates that are made by the Apply program for an update-anywhere subscription set. The Capture program derives this value from the critical section table. |
Important: Do not use SQL to update this table. Altering this table inappropriately can cause unexpected results and loss of data.
CD
Change data (CD) tables record all changes made to a replication source. Committed, uncommitted, and incomplete changes are inserted as rows into the CD table. The CD table works with the UOW table to provide commit information. (See Staging data for more information.) Pruning of the CD table rows is coordinated by the pruning control table. (See Pruning control table for more information.)
CD tables are automatically created when you define a replication source. For each replication source that is enabled for data capture, there is one CD table. If you cold start the Capture program, all of the CD table's entries are deleted.
Manually changing the CD table is not recommended. However, the CD table can be a useful resource for problem determination. Knowing exactly what changes were committed or not committed can help you understand where the Capture program failed.
Recommendation: A unique ascending index is strongly recommended for the IBMSNAP_UOWID and IBMSNAP_INTENTSEQ columns.
Table 51 provides a list and a brief description of each of the
columns in the CD table.
Table 51. Columns in the CD table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| IBMSNAP_UOWID | Unit-of-work ID for an update. The Apply program uses this column to join the CD table with the UOW table so that only committed changes are replicated. |
| IBMSNAP_INTENTSEQ | Log or journal record sequence number that uniquely identifies a change. This value is globally ascending. |
| IBMSNAP_OPERATION | Character value of I, U, or D, indicating an insert, update, or delete record. |
| DATA1 | User column from source table specified when the replication source was defined. |
| AFTER-IMAGE | User column from source table selected when defining a replication source. This column will have the same name, data type, and null attributes as the source column. The after-image column also contains the equivalent source table column value after the change is made. |
| BEFORE-IMAGE | User column from source table selected when defining a replication source. This column will have the same name, data type, and null attributes as the source column. The name is the source column prefixed with the BEFORE_IMG_PREFIX value from the register table. This column contains the equivalent source table column value before the change was made. |
The control server is the DB2 system that you chose to hold your subscription definitions. The following section provides a brief description of the tables used at the control server and the columns in each table. If you are using the Control Center, these tables, which contain information about your subscription definitions, are automatically created when you define a subscription set if they do not already exist.
The subscription set, subscription-targets-member, subscription columns, subscription statements, row-replica, and subscription-schema-changes tables contain information about subscriptions. When a new subscription set is defined, the administration tools simultaneously update rows in the subscription set, subscription columns, subscription-targets-member, and subscription statements tables.
The subscription events and Apply trail tables are used by the Apply program to control and audit your data.
Important: Do not use SQL to update this table. Altering this table inappropriately can cause unexpected results and loss of data.
ASN.IBMSNAP_SUBS_SET
The subscription set table lists all of the subscription sets defined at the control server and identifies the source and target server pairs that are processed as a group. Rows are inserted into this table when you create your subscription set definition.
Use this table to identify subscription sets that are defined.
Table 52 provides a brief description of the columns in the
subscription set table.
Table 52. Columns in the subscription set table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| APPLY_QUAL | Uniquely identifies a group of subscription sets that are processed by the same Apply process. This user-specified value must be unique for the control server where the subscription set table is located. For update-anywhere, this value must be unique at the control server and at the source server. This value is case-sensitive. You must specify this value when you define a subscription set. See Defining replication subscription sets for more details. |
| SET_NAME | Identifies a group of source and target tables (subscription-set members) that are processed by the Apply program as a group. This user-specified value must be unique within an Apply qualifier. Changes for subscription members in a set are processed in a single transaction during the Apply processing cycle. |
| WHOS_ON_FIRST | The following values are used to control the order of processing in
update-anywhere replication scenarios.
|
| ACTIVATE | The following values are flags set by either the administration tool
(0 and 1) or by the Apply program (2).
|
| SOURCE_SERVER | The database name of the source server where the source tables and views are defined. |
| SOURCE_ALIAS | The DB2 Universal Database alias corresponding to the source server named in the SOURCE_SERVER column. |
| TARGET_SERVER | The database name of the server where the target tables and views are defined. |
| TARGET_ALIAS | The DB2 Universal Database alias corresponding to the target server named in the TARGET_SERVER column. |
| STATUS | A value that represents in-progress and completed work status for the
Apply program.
|
| LASTRUN | The estimated time that the last subscription set began. The Apply program sets the LASTRUN value each time a subscription set is processed. It is the approximate time at the control server that the Apply program begins processing the subscription set. |
| REFRESH_TIMING | Sets the timing between statement executions.
|
| SLEEP_MINUTES | Specifies the time (in minutes), of inactivity between subscription set processing when REFRESH_TIMING is R or B. |
| EVENT_NAME | A unique character string used to represent an event. Use this identifier to update the subscription events table when you want to trigger replication for a subscription set. |
| LASTSUCCESS | The control server timestamp for the beginning of the last successful processing of a subscription set. |
| SYNCHPOINT | The Apply program uses the SYNCHPOINT value from the global row of the register table at the source server if GLOBAL_RECORD is Y. If data blocking is specified in the subscription-set definition, then the SYNCHPOINT value is the log or journal record sequence number of the last change applied during the Apply process. |
| SYNCHTIME | The Capture program or an external program, such as IMS
DataPropagator, updates this timestamp whether there are changes to be
processed or not.
The Apply program uses this value when advanced conflict detection is selected for update-anywhere replication to ensure that the Capture program captured all outstanding changes for a replication source table. |
| MAX_SYNCH_MINUTES | A time-threshold limit to regulate the amount of change data to fetch and apply during a subscription cycle. The Apply program breaks the subscription set processing into mini-cycles based on the IBMSNAP_LOGMARKER column in the UOW or CCD table at the source server and issues a COMMIT at the target server after each successful mini-cycle. The limit is automatically recalculated if the Apply program encounters a resource constraint that makes the set limit unfeasible. MAX_SYNCH_MINUTES values that are less than 1 will be treated the same as a MAX_SYNCH_MINUTES value equal to NULL. |
| AUX_STMTS | The number of SQL statements that you define in the subscription statement table that can run before or after the Apply program processes a subscription set. |
| ARCH_LEVEL | The architectural level of the definition contained in the row. This field identifies the rules under which a row was created. This level is defined by IBM, and for Version 7 is 0201. |
Important: Do not use SQL to update this table. Altering this table inappropriately can cause unexpected results and loss of data.
ASN.IBMSNAP_SUBS_MEMBR
This table or view contains information about the individual source and target table pairs defined for a subscription set. Rows are automatically inserted into this table when you create a subscription set member.
Use this table or view to identify a specific source and target table pair within a subscription set.
Table 53 provides a brief description of the columns in the
subscription-targets-member table.
Table 53. Columns in the subscription-targets-member table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| APPLY_QUAL | Uniquely identifies a group of subscription sets that are processed by the same Apply process. This user-specified value must be unique for the control server where the subscription set table is located. For update-anywhere, this value must be unique at the control server and at the source server. This value is case-sensitive. You must specify this value when you define a subscription set. |
| SET_NAME | Identifies a group of source or target table pairs (subscription-set members) that are processed by the Apply program as a group. This user-specified value must be unique within an Apply qualifier. Changes for subscription members in a set are processed in a single transaction during the Apply processing cycle. |
| WHOS_ON_FIRST | The following values are used to control the order of processing in
update-anywhere replication scenarios.
|
| SOURCE_OWNER | The owner of the source table or view. |
| SOURCE_TABLE | The source from which data is being captured. |
| SOURCE_VIEW_QUAL | Supports the view of physical tables by matching the similar column in the register table. This value is set to 0 for physical tables that are defined as sources and is greater than 0 for views that are defined as sources. This column is used to support multiple subscriptions for different source views with identical SOURCE_OWNER and SOURCE_TABLE column values. |
| TARGET_OWNER | A qualifier for a target table or view. |
| TARGET_TABLE | The target to which data is being applied. |
| TARGET_CONDENSED | A flag indicating:
|
| TARGET_COMPLETE |
A flag indicating:
|
| TARGET_STRUCTURE | The structure of the target table:
|
| PREDICATES | Lists the predicates to be placed in a WHERE clause for the table in the TARGET_TABLE column. This WHERE clause creates a row subset of the source table. Predicates are recognized only when WHOS_ON_FIRST is set to S. The letter A is a predefined correlation-name for the physical source table used in a correlated subquery. Cannot contain an ORDER BY clause because the Apply program cannot generate an ORDER BY clause. Aggregate tables require a dummy predicate followed by a GROUP BY clause as a predicate. |
Important: Do not use SQL to update this table. Altering this table inappropriately can cause unexpected results and loss of data.
ASN.IBMSNAP_SUBS_COLS
This table contains information about the columns of the subscription-set members being copied in a subscription set. The subscription columns table contains supplemental information to the subscription-targets-member table.
Rows are automatically inserted or deleted from this table when information contained in one or more columns of a source and target table pair is changed.
Use this table if you need information about specific columns in a subscription-set member.
Table 54 provides a brief description of the columns in the
subscription columns table.
Table 54. Columns in the subscription columns table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| APPLY_QUAL | Identifies the Apply program for the platform instance that will run this subscription set. The value must be unique among all Apply processes maintaining dependent replicas of a user table or parent replica, and unique among all Apply processes sharing a common set of control tables. This value is case sensitive. You must specify this value when you define a subscription set. |
| SET_NAME | Names a subscription set. This value is unique within an Apply qualifier. |
| WHOS_ON_FIRST | The following values are used to control the order of processing in
update-anywhere replication scenarios.
|
| TARGET_OWNER | A qualifier for a target table or view. |
| TARGET_TABLE | The target to which data is being applied. |
| COL_TYPE |
A flag indicating:
|
| TARGET_NAME | The name of the target table or view column. It does not need
to match the source column name.
Internal CCD column names cannot be renamed. They must match the CD table column names. |
| IS_KEY |
|
| COLNO | The numeric location of the column in the original source, to be preserved relative to other user columns in displays and subscriptions. |
| EXPRESSION | The source column name or an SQL expression representing the target column. |
Important: Do not use SQL to update this table. Altering this table inappropriately can cause unexpected results and loss of data. The number of entries for a subscription should be reflected in ASN.IBMSNAP_SUBS_SET.AUX_STMTS. If AUX_SMTS is zero for a subscription set, the corresponding entries in the subscription statements table are ignored by the Apply program.
ASN.IBMSNAP_SUBS_STMTS
This table contains the user-defined SQL statements or stored procedure calls that will be executed before or after each subscription-set processing cycle. Execute immediately (EI) statements or stored procedures can be executed at the source or target server only. This table is populated when you define a subscription set that uses SQL statements or stored procedure calls.
Table 55 provides a brief description of the columns in the
subscription statements table.
Table 55. Columns in the subscription statements table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| APPLY_QUAL | Uniquely identifies a group of subscription sets that are processed by the same Apply process. This user-specified value must be unique for the control server where the subscription set table is located. For update-anywhere, this value must be unique at the control server and at the source server. This value is case-sensitive. You must specify this value when you define a subscription set. |
| SET_NAME | Identifies a group of source and target table pairs (subscription-set members) that are processed by the Apply program as a group. This user-specified value must be unique within an Apply qualifier. Changes for subscription-set members in a set are processed in a single transaction during the Apply processing cycle. |
| WHOS_ON_FIRST | The following values are used to control the order of processing in
update-anywhere replication scenarios.
|
| BEFORE_OR_AFTER | A value indicating:
|
| STMT_NUMBER | Defines the relative order of execution within the scope of BEFORE_OR_AFTER. |
| EI_OR_CALL | A value indicating:
|
| SQL_STMT | One of the following values:
|
| ACCEPT_SQLSTATES | One to ten 5-byte SQLSTATE values that you specified when you defined the subscription set. These non-zero values are accepted by the Apply program as a successful execution. Any other values will cause a failed execution. |
Important: Do not use SQL to update this table. Altering this table inappropriately can cause unexpected results and loss of data.
ASN.IBMSNAP_SUBS_TGTS
This table is necessary to identify when a member has been deleted from a subscription set for a Microsoft Jet database target, so that the row-replica table can be deleted from the Microsoft Jet database. The row-replica-target-list table allows DataPropagator for Microsoft Jet to maintain a list of known row-replica tables in a stable DB2 or DataJoiner database. DataPropagator for Microsoft Jet uses this information during schema analysis to determine if any row-replica tables should be deleted because the corresponding subscription-set member was dropped since the last synchronization.
Table 56 provides a brief description of the columns in the
row-replica-target-list table.
Table 56. Columns in the row-replica-target-list table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| APPLY_QUAL | Uniquely identifies a group of subscription sets that are processed by the same Apply process. This user-specified value must be unique for the control server where the subscription set table is located. For update-anywhere, this value must be unique at the control server and at the source server. This value is case-sensitive. You must specify this value when you define a subscription set. |
| SET_NAME | Identifies a group of source and target table pairs (subscription-set members) that are processed by the Apply program as a group. This user-specified value must be unique within an Apply qualifier. |
| WHOS_ON_FIRST | The following values are used to control the order of processing in
update-anywhere replication scenarios.
|
| TARGET_OWNER | A qualifier for a target table or view. |
| TARGET_TABLE | The target to which data is being applied. |
| LAST_POSTED | This column is the timestamp of when this row was inserted into the table. This column is for informational purposes only. |
Important: Do not use SQL to update this table. Altering this table inappropriately can cause unexpected results and loss of data.
ASN.IBMSNAP_SCHEMA_CHG
This table allows DataPropagator for Microsoft Jet to determine if some relevant schema change has occurred since its last synchronization. If a modification is made, DataPropagator for Microsoft Jet will drive a thorough analysis of the replication control information. DataPropagator for Microsoft Jet will then create or drop row-replica tables, or columns in row-replica tables, to automatically converge the Microsoft Jet database schema with the schema described by the replication control information. This schema convergence occurs before data synchronization, so that new columns and new tables are copied.
Table 57 provides a brief description of the columns in the
subscription-schema-changes table.
Table 57. Columns in the subscription-schema-changes table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| APPLY_QUAL | Uniquely identifies a group of subscription sets that are processed by the same Apply process. This user-specified value must be unique for the control server where the subscription set table is located. For update-anywhere, this value must be unique at the control server and at the source server. This value is case-sensitive. You must specify this value when you define a subscription set. |
| SET_NAME | Identifies a group of source and target table pairs (subscription-set members) that are processed by the Apply program as a group. This user-specified value must be unique within an Apply qualifier. Changes for subscription members in a set are processed in a single transaction at the target site during the Apply processing cycle. |
| LAST_CHANGED | This column is the timestamp of when this row was last changed in this table. This column is for informational purposes only. |
This table contains information that you update using SQL.
ASN.IBMSNAP_SUBS_EVENT
This table contains information about the event triggers that are copied in a subscription set. The subscription events table contains event names and timestamps associated with the event names. You insert a row into this table when you create a new event to start an Apply process. See Event timing.
Table 58 provides a brief description of the columns in the
subscription events table.
Table 58. Columns in the subscription events table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| EVENT_NAME | When you replicate events between systems, this column contains a globally unique character string in a global name space configuration. Otherwise, this column contains a control server unique character string. |
| EVENT_TIME | A control server timestamp of a current or future posting time. User applications signalling replication events provide the values in this column. |
| END_OF_PERIOD | A source server timestamp value that acts like an upper boundary.
Any transactions that are committed after this period are not replicated until
a later event is posted.
The only way to prevent eligible change data from replicating during a subscription cycle is to make sure that the value in this column is less than the CURRENT TIMESTAMP value at the source server. |
A unique index on EVENT_NAME and EVENT_TIME is created automatically by the administration tool or by the DPCNTL file.
ASN.IBMSNAP_APPLYTRAIL
The Apply trail table contains audit trail information for the Apply program. This table records a history of updates performed against subscriptions. It is a repository of diagnostic and performance statistics. The Apply trail table is one of the best places to look if a problem occurs with the Apply program. Because this table is not automatically pruned, it is up to you to do so.
Table 59 provides a brief description of the columns in the Apply
trail table.
Table 59. Columns in the Apply trail table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| APPLY_QUAL | Uniquely identifies a group of subscription sets that are processed by the same Apply process. This user-specified value must be unique for the control server where the subscription set table is located. For update-anywhere, this value must be unique at the control server and at the source server. This value is case-sensitive. You must specify this value when you define a subscription set. |
| SET_NAME | Identifies a group of source and target table pairs (subscription-set members) that are processed by the Apply program as a group. This user-specified value must be unique within an Apply qualifier. Changes for subscription members in a set are processed in a single transaction at the target site during the Apply program processing cycle. |
| WHOS_ON_FIRST | The following values are used to control the order of processing in
update-anywhere replication scenarios.
|
| ASNLOAD | Contains one of the following values:
|
| MASS_DELETE | A mass delete is always triggered during a full refresh. The
following are values for this column:
|
| EFFECTIVE_MEMBERS | The number of subscription-set members that are changed during an Apply cycle, either by a full refresh or by the replication of inserts, updates, and deletes. This number ranges between zero and the number of defined subscription-set members. |
| SET_INSERTED | The total number of rows inserted into subscription-set members during the subscription cycle. |
| SET_DELETED | The total number of rows deleted from subscription-set members during the subscription cycle. |
| SET_UPDATED | The total number of rows updated in subscription-set members during the subscription cycle. |
| SET_REWORKED | The Apply program reworks changes under the following conditions:
|
| SET_REJECTED_TRXS | The total number of transactions rejected due to an update-anywhere conflict. This column is used only for update-anywhere subscription sets where conflict detection is defined as standard or advanced. |
| STATUS | A value that represents in-progress and completed work status for the
Apply program.
|
| LASTRUN | The estimated time that the last subscription began. The Apply program sets the LASTRUN value each time a subscription set is processed. It is the approximate time at the control server that the Apply program begins processing the subscription set. |
| LASTSUCCESS | The control server timestamp for the beginning of the last successful processing of a subscription set. |
| SYNCHPOINT | The Apply program uses the SYNCHPOINT value from the global row of the register table at the source server if GLOBAL_RECORD is Y. If data blocking is specified in the subscription definition, then the SYNCHPOINT value is the log or journal record sequence number of the last change applied during the Apply process. |
| SYNCHTIME | The Capture program or an external program, such as IMS
DataPropagator, updates this timestamp whether there are changes to be
processed or not.
The Apply program uses this value when advanced conflict detection is selected for update-anywhere replication to ensure that the Capture program has captured all outstanding changes for a replication source table. |
| SOURCE_SERVER | The database name of DB2 for OS/390, DB2 for VSE, and DB2 for VM where the source tables and views are defined. |
| SOURCE_ALIAS | The DB2 Universal Database alias corresponding to the source server named in the SOURCE_SERVER column. |
| SOURCE_OWNER | The owner of the source table or view. |
| SOURCE_TABLE | The source from which data is being captured. |
| SOURCE_VIEW_QUAL | Supports the view of physical tables by matching the similar column in the register table. This value is set to 0 for physical tables that are defined as sources and is greater than 0 for views that are defined as sources. This column is used to support multiple subscriptions for different source views with identical SOURCE_OWNER and SOURCE_TABLE column values. |
| TARGET_SERVER | The database name of the target server where the target tables and views are defined. |
| TARGET_ALIAS | The DB2 Universal Database alias corresponding to the target server named in the TARGET_SERVER column. |
| TARGET_OWNER | A qualifier for a target table or view. |
| TARGET_TABLE | The target to which data is being applied. |
| SQLSTATE | The SQL state code for a failed execution. Otherwise, NULL. |
| SQLCODE | The SQL error code for a failed execution. Otherwise, NULL. |
| SQLERRP | The database product identifier of the server where an SQL error occurred that caused a failed execution. Otherwise, NULL. |
| SQLERRM | The SQL error information for a failed execution. Otherwise, NULL. |
| APPERRM | The Apply error message ID and text for a failed execution. Refer to Capture and Apply messages and Replication messages for AS/400 for detailed message information. Otherwise, NULL. |
Important: Do not use SQL to update this table. Altering this table inappropriately can cause unexpected results and loss of data.
IBMSNAP_APPLY_JOB
This AS/400-specific table is used to guarantee a unique APPLY_QUAL value for all instances of the Apply program running at the control server. A row is added to this table every time an instance of the Apply program is started. If you start a new instance of the Apply program with an APPLY_QUAL value that already exists, the start command fails.
Table 60 provides a brief description of the columns in the Apply job
table.
Table 60. Columns in the Apply job table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| APPLY_QUAL | A unique identifier for a group of subscription sets. This value is supplied by the user when defining a subscription set. Each instance of the Apply program is started with an APPLY_QUAL. This value is used during update-anywhere replication to prevent circular replication of the changes made by the Apply program. See the subscription set table on page Subscription set table for more details. |
| CONTROL_SERVER | Name of the database where the control tables and view are defined. |
| USER_NAME | Name of the user who started a new instance of the Apply program |
| JOB_NAME | The fully qualified name of the job that wrote this trace entry:
|
| JOB_NUMBER | The job number of the current job for a particular journal. If the journal is not active, this column contains the job number of the last job that was processed. |
The following section provides a brief description of the types of target tables used at the target server and the columns in each table.
Important: If you use SQL to update this table, you run the risk of losing your updates when a full refresh is performed by the Apply program.
userid.target_table
The user copy table is identical to the point-in-time target table with the exception of the IBMSNAP_LOGMARKER column, which is not included in the user copy table.
Except for subsetting and data enhancement, a user copy table reflects a valid state of the source table, but not necessarily the most current state. References to user copy tables (or any other type of target table) reduce the risk of contention problems that results from a high volume of direct access to the source tables. Accessing local user copy tables is much faster than using the network to access remote source tables for each query.
Table 61 provides a brief description of the columns in the user copy
table.
Table 61. Columns in the user copy table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| user key columns | The primary key of the target table, although it is not necessarily a component of the primary key of the source table. You can use predicates to prevent a NULL value from being assigned to the key fields of any copies. |
| user nonkey columns | The nonkey data columns from the source table or view. The columns from the source table do not need to match these columns, but the data types must match. |
| user computed columns | User-defined columns that are derived from SQL expressions. You can use computed columns with SQL functions to convert source data types to different target data types. |
Important: If you use SQL to update this table, you run the risk of losing your updates when a full refresh is performed by the Apply program.
userid.target_table
The point-in-time table is similar to the user copy table, but contains an additional system column (IBMSNAP_LOGMARKER) containing the approximate timestamp of when the particular row was inserted or updated at the source system. Otherwise, a point-in-time table is much like a past image of the source table. Point-in-time copies reflect a valid state of the source table, but not necessarily the most current state.
Table 62 provides a brief description of the columns in the
point-in-time table.
Table 62. Columns in the point-in-time table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| user key columns | The primary key of the target table, although it is not necessarily a component of the primary key of the source table. You can use predicates to prevent a NULL value from being assigned to the key fields of any copies. |
| user nonkey columns | The nonkey data columns from the source table or view. The columns from the source table do not need to match these columns, but the data types must match. |
| user computed columns | User-defined columns that are derived from SQL expressions. You can use computed columns with SQL functions to convert source data types to different target data types. |
| IBMSNAP_LOGMARKER | The approximate commit time at the source server. This column is NULL following a full refresh. |
This table contains information that you can update by using SQL.
userid.target_table
CCD tables are staging tables that contain committed change data (for details, see Staging data). Maintaining CCD tables requires updating the CCD_OLD_SYNCHPOINT and SYNCHPOINT columns of the register table.
The CCD table can be:
The result of a join between the CD and UOW tables can be stored here, so that you perform the join step only once for replicating changes to multiple targets. The CCD table can be maintained on a remote system. The advantage of maintaining your CCD table remotely is that you reduce the work load on your source. You replicate a set of changes from the original source to the CCD table only once. The CCD table then acts as the source and maintains all changes.
External programs can create CCD tables to be used by DB2 DataPropagator as replication sources. An example is IMS DataPropagator, which captures IMS changes and maintains a CCD table so that copies of IMS data can be recreated in a relational database.
For CCD tables:
The originally captured operation code in the IBMSNAP_OPERATION column and the sequence numbers IBMSNAP_INTENTSEQ and IBMSNAP_COMMITSEQ are included in CCD tables. For condensed CCD tables, only the latest values are kept for each row.
Special cases for condensed CCD tables
Because condensed CCD tables must have a unique index:
Table 63 provides a brief description of the columns in the CCD
table.
Table 63. Columns in the CCD table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| IBMSNAP_INTENTSEQ | Log or journal record sequence number that uniquely identifies a change. This value is globally ascending. |
| IBMSNAP_OPERATION | Character value of I, U, or D, indicating an insert, update, or delete record. |
| IBMSNAP_COMMITSEQ | The log record sequence number of the captured commit statement. This value groups inserts, updates, and deletes by the original transactions for the source table. |
| IBMSNAP_LOGMARKER | The approximate commit time at the source server. |
| user key columns | The primary key of the target table, although it is not necessarily a component of the primary key of the source table. You can use predicates to prevent a NULL value from being assigned to the key fields of any copies. |
| user nonkey columns | The nonkey data columns from the source table. The columns from the source table do not need to match these columns, but the data types must match. |
| user computed columns | User-defined columns that are derived from SQL expressions. You can use computed columns with SQL functions to convert source data types to different target data types. |
This table contains information that you can update by using SQL.
userid.target_table
The replica must have the same primary key as the source table. Because of these similarities, the replica table can be used as a source table for further subscription sets, making the target server a source server as well. Converting a target table into a source table is done automatically when you define a replica target type and specify the CHANGE DATA CAPTURE attribute. See Defining subscription sets for update-anywhere replication for more information.
Table 64 provides a brief description of the columns in the replica
table.
Table 64. Columns in the replica table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| user key columns | The primary key of the target table, although it is not necessarily a component of the primary key of the source table. You can use predicates to prevent a NULL value from being assigned to the key fields of any copies. |
| user nonkey columns | The nonkey data columns from the source table. The columns from the source table do not need to match these columns, but the data types must match. |
userid.target_table
Base aggregate tables are target tables that contain data aggregated from a source table. Functions are performed on data located at the source table, and the result of the function is inserted as a row in the base aggregate table.
For base aggregate tables:
Table 65 provides a brief description of the columns in the base
aggregate table.
Table 65. Columns in the base aggregate table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| user columns | Columns computed from the source table. |
| IBMSNAP_LLOGMARKER | The current source server timestamp when the data was last aggregated. |
| IBMSNAP_HLOGMARKER | The current source server timestamp when the data was last aggregated. |
Important: Do not use SQL to update this table. Altering this table inappropriately can cause unexpected results and loss of data.
userid.target_table
A change aggregate table is a target table that contains data aggregations based on changes from a source table. This table is similar to the base aggregate table, except that the functions being performed at the source table are done only for changes that occur during a specific time interval. The results of these functions are inserted as rows into the change aggregate table. Before-image user data columns must be nullable in change aggregate tables.
Table 66 provides a brief description of the columns in the change
aggregate table.
Table 66. Columns in the change aggregate table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| user key columns | The primary key of the target table, although it is not necessarily a component of the primary key of the source table. You can use predicates to prevent a NULL value from being assigned to the key fields of any copies. |
| user nonkey columns | The nonkey data columns from the source table. The columns from the source table do not need to match these columns, but the data types must match. |
| user computed columns | User-defined columns that are derived from SQL expressions. You can use computed columns with SQL functions to covert source data types to different target data types. |
| IBMSNAP_LLOGMARKER | The oldest IBMSNAP_LOGMARKER or IBMSNAP_LLOGMARKER value present in the (CD+UOW) or CCD table rows being aggregated. |
| IBMSNAP_HLOGMARKER | The newest IBMSNAP_LOGMARKER or IBMSNAP_HLOGMARKER value present in the (CD+UOW) or CCD table rows being aggregated. |
Important:This table contains information that you can update by using SQL.
userid.target_table
This table is an update-anywhere replica table maintained by DataPropagator for Microsoft Jet. Conflicts are detected row by row, not transaction by transaction, as they are for replica tables. Row-replica is the only type of target table supported by DataPropagator for Microsoft Jet. The source table can be a DB2, Oracle, Sybase, Informix, or Microsoft SQL Server user table, or a DB2 replica. The source can also be a view of a DB2 user table or replica table, including a join view.
Table 67 provides a brief description of the columns in the
row-replica table.
Table 67. Columns in the row-replica table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| user key columns | The primary key of the target table, although it is not necessarily a component of the primary key of the source table. You can use predicates to prevent a NULL value from being assigned to the key fields of any copies. |
| user nonkey columns | The nonkey data columns from the source table. The columns from the source table do not need to match these columns, but the data types must match. |
Important: Do not use SQL to update this table. Altering this table inappropriately can cause unexpected results and loss of data.
IBMSNAP_<target name>_CONFLICT
This table is a conflict table for tracking synchronization conflicts and errors. This Microsoft Jet database control table mimics Microsoft's conflict tables. This table contains the conflict loser's row data. The columns are the same as the corresponding row-replica table. This table can have more than one row. The conflict table is created along with the row-replica table in the Microsoft Jet database and dropped when the row-replica table is dropped.
Table 68 provides a brief description of the columns in the conflict
table.
Table 68. Columns in the conflict table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| target name | The corresponding row-replica table's name. |
| column names of row-replica | A list of column names found in the corresponding row-replica table. |
Important: Do not use SQL to update this table. Altering this table inappropriately can cause unexpected results and loss of data.
IBMSNAP_ERROR_INFO
This table identifies the row-replica table and row that caused the error. This table can have more than one row. The error information table is created along with the Microsoft Jet database and never dropped.
Table 69 provides a brief description of the columns in the error
information table.
Table 69. Columns in the error information table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| TableName | The name of the row-replica table that is the source of the row that caused the error. |
| RowGuid | The GUID of the row that caused the error. |
| Operation | One of the following commands to identify the operation that caused the error: INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE. |
| Reason | The DB2 DataPropagator error message number. |
Important: Do not use SQL to update this table. Altering this table inappropriately can cause unexpected results and loss of data.
IBMSNAP_ERROR_MESSAGE
This table identifies the nature of an error. It contains the error code and error message. This table can have more than one row. The error messages table is created along with the Microsoft Jet database and never dropped.
Table 70 provides a brief description of the columns in the error
messages table.
Table 70. Columns in the error messages table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| Reason | The DB2 DataPropagator error message number. |
| ReasonText | The DB2 DataPropagator error message text. |
Important: Do not use SQL to update this table. Altering this table inappropriately can cause unexpected results and loss of data.
IBMSNAP_SIDE_INFO
This table is a conflict table for tracking synchronization conflicts and errors. This Microsoft Jet database control table mimics Microsoft's conflict tables. This table contains the names of the conflict tables created by DataPropagator for Microsoft Jet.
Table 71 provides a brief description of the error-side-information
table column.
Table 71. Error-side-information table column
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| ConflictTableName | The conflict table name created by DataPropagator for Microsoft Jet. |
Important: Do not use SQL to update this table. Altering this table inappropriately can cause unexpected results and loss of data.
IBMSNAP_GUID_KEY
This table maps the Microsoft Jet table names and row identifiers to primary key values when the following changes occur:
Table 72 provides a brief description of the columns in the key
string table.
Table 72. Columns in the key string table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| RowReplicaname | Identifies the row-replica table where the row was inserted. |
| s_GUID | Identifies the row in the specific row-replica table. |
| key_string | The string of "and-ed" DB2 SQL predicates identifying the key columns and
their row values, with character constants delimited by single quotation
marks. The column names are taken from the row-replica definition and
can contain uppercase letters, lowercase letters or both. The constant
values are taken from the rows themselves and the string values can contain
uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numeric characters, or any combination
of the three. Microsoft Jet database supports ASCII, so the string
constants can contain single- or double-byte characters. For
example:
COL1=(character) AND COL2=(character) |
Important: Do not use SQL to update this table. Altering this table inappropriately can cause unexpected results and loss of data.
IBMSNAP_S_GENERATION
This table is used to prevent cyclic updates from replicating back to the RDBMS from a Microsoft Jet database. When DB2 is the target, this function is accomplished in a different way, using the APPLY_QUAL column of the critical section table, which results in the Capture Program posting to the APPLY_QUAL column of the UOW table.
The s_GENERATION column is maintained by Microsoft Jet and set to the same generation number as any other updates made since the last synchronization. If synchronization is successful, the synchronization generations table will contain one row whose Update_Type value is F.
Due to the risk of partial failures during a DataPropagator for Microsoft Jet synchronization cycle, and because the WHOS_ON_FIRST = S flow is handled before the WHOS_ON_FIRST = F flow, multiple RDBMS-to-Jet generations can be posted before any Microsoft Jet database changes replicate to the RDBMS. In such a case, there is the possibility that a list of s_GENERATION values will need to be skipped over when determining which s_GENERATION of changes needs to be replicated to the RDBMS.
Table 73 provides a brief description of the columns in the
synchronization generations table.
Table 73. Synchronization generations table
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| Update_Type | A value that indicates whether a generation of changes is:
|
| JetSynchtime | This is a dummy column, set to the time of a forced Microsoft Jet database synchronization. |