

In this step, you will configure the Credential Mapper Servlet (CMS). The CMS is supplied with Host On-Demand and must be deployed to a J2EE-compliant Web application server. At a high level, the CMS is responsible for the following tasks: (1) determine the client's identity (called a network ID), (2) map the user's network ID to the host ID, and (3) return the host credentials to the client as an XML document.
Host On-Demand provides three CMS WAR files, one for each of the following network security applications:
|
If you have a different network security application, you will need to customize your own version of the CMS. For more information about how to do this, refer to Customizing Web Express Logon (opens new browser). |
In addition to several CLASS files, the WAR file contains the following four files:
The web.xml file is the servlet configuration file that you will edit in this step. The other two XML files (DCAS.xml and Vault.xml) are sample files that Host On-Demand provides to help you better understand DCAS and Vault parameters and their values. These two XML files can also serve as a valuable reference when you edit the web.xml file. We also recommend that you use these files as a reference when you edit the web.xml file. Finally, the was.policy file is for IBM WebSphere Application Server only. It contains the required permissions for the CMS when Java 2 security is enabled. For more information, refer to Troubleshooting Web Express Logon (opens new browser)
Take the following steps to begin configuring the CMS:
1. Locate the WAR file on the Host On-Demand CD.
With the Host On-Demand V8 CD loaded in the CD drive of your machine, take the following steps to locate the WAR files on the CD.
| Network security application | Corresponding WAR file |
| IBM Tivoli Access Manager for e-business V4.1 | amcms.war |
| Netegrity Siteminder V5.5 | smcms.war |
| Microsoft Active Directory (Windows Domain) | wincms.war |
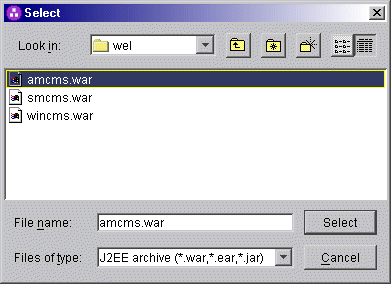
Highlight the WAR that represents
your network security application and press Select.
Then select OK.
|
If you have a different network security application, you will need to customize your own version of the CMS. For more information about how to do this, refer to Customizing Web Express Logon (opens new browser). |
2. Edit the CMS-related parameters.
In this step, you will edit two of
the three INIT parameters in the web.xml file. You will not edit the CMPINetworkSecurity
parameter name or value.
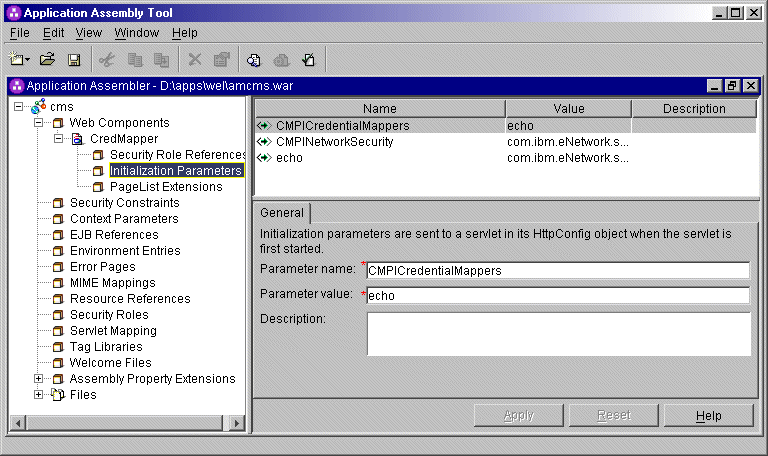
CMPICredentialMappers,
and the parameter value is a compound value that contains the list of all
available HCMs, for example, CMPIDCASPlugin and CMPIVaultPlugin.
Currently, the value is echo, but you will eventually replace
this with the name of your HCM plug-in. <init-param>
<param-name>CMPICredentialMappers</param-name>
<param-value>echo</param-value>
</init-param> CMPINetworkSecurity,
and the parameter value is the full path name of the class that handles the
CMS interface into the network security application, which is Tivoli Access
Manager in this scenario. <init-param>
<param-name>CMPINetworkSecurity</param-name>
<param-value>com.ibm.eNetwork.security.sso.cms.CMNPIAccessManager</param-value>
</init-param>
|
The Network Security plug-in does not apply to Microsoft Active Directory XML file (wincms.xml) since the Windows login ID is used as the network ID. |
echo
plug-in: The name of this INIT parameter (echo) is
the same as the value for the HCM plug-in. In a future step, you will replace
echo with the name of your HCM.|
Some Web application server products allow you to deploy the servlet first and then edit the XML file. Other products, such as WebSphere Application Server V5, work best when you deploy the servlet after you edit the XML code. Refer to your product's documentation for details. |
<init-param>
<param-name>echo</param-name>
<param-value>com.ibm.eNetwork.security.sso.cms.CMPINetEcho,AuthType_All,*</param-value>
</init-param>
CMPICredentialMappers
parameter in the top panel of the window. In the Parameter
value field below, change the name of its current value (echo)
to the name of your HCM plug-in. In this scenario, the administrator specifies
CMPIVaultPlugin as the parameter value because he is using a
vault-style database as his HCM plug-in. Optionally provide a description
and click Apply to replace the value in the top
window.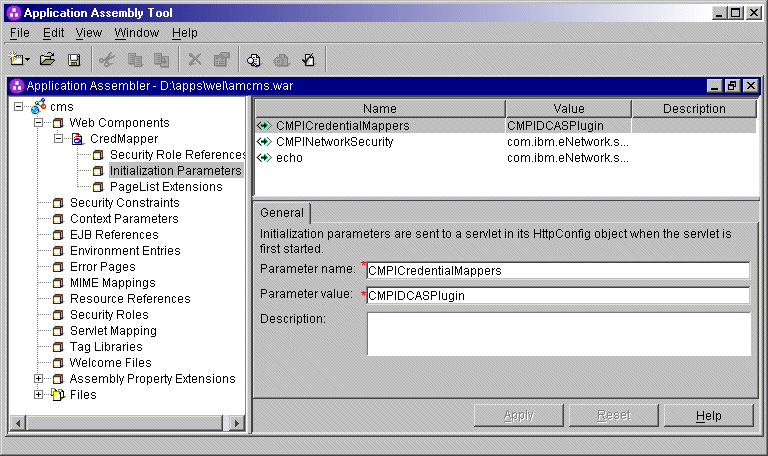
Code example:
<init-param>
<param-name>CMPICredentialMappers</param-name>
<param-value>CMPIDCASPlugin</param-value>
</init-param>
Highlight the echo
parameter in the top panel of the window. In the Parameter
name field below, replace the current parameter name (echo)
with the name of the parameter value that you specified for the HCM plug-in.
In this scenario, the administrator changed the parameter name to CMPIVaultPlugin.
Now, replace the parameter value
with a compound value that contains the full class path name of the implementing
class, the authentication type to be used by the HCM plug-in, and the host
mask. Separate these values with commas. In this scenario, the administrator
added com.ibm.eNetwork.security.sso.cms.CMPIVault for the full
class path name, AuthType_3270Host for the authentication type,
and * for the host mask. Optionally
provide a description and click Apply to replace
the value in the top window.
|
The authentication type for FTP sessions should be either AuthType_FTPPassword or AuthType_All. |
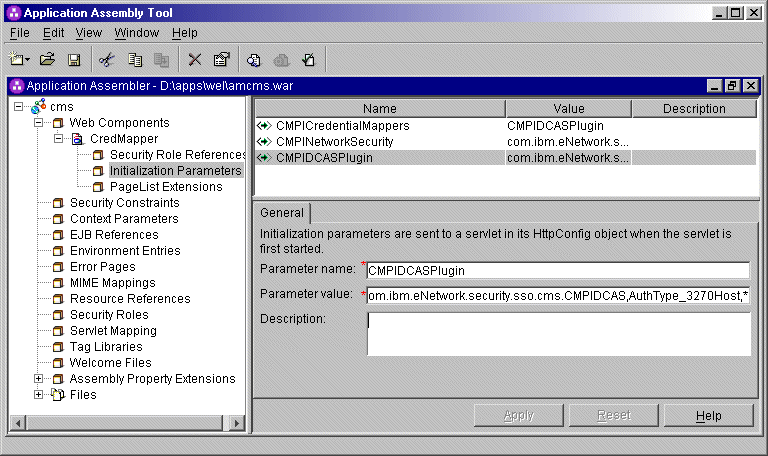
<init-param>
<param-name>CMPIDCASPlugin</param-name>
<param-value>com.ibm.eNetwork.security.sso.cms.CMPIDCAS,AuthType_3270Host,*</param-value>
</init-param> | Full class path
name The CMS uses the value of the full class path name to create a class object of the specified type. That object is then used to handle CMS or HCM plug-in requests. The specified class file must be in the ...\WEB-INF\classes subdirectory in a loose file (not as a JAR file). From this location, the CMS will be able to access and use it whenever the need arises. Authentication type This parameter value is used to identify the type of authentication that the requestor needs. Once you specify the desired authentication type, the CMS can better identify which HCM plug-in to select to handle the request. You can pair multiple authentication types together to give HCM plug-ins the freedom to support multiple authentication types. Use the vertical bar character to join multiple authentication types. The five identified authentication types and descriptions are listed in the following table:
Host mask
|
3. Add optional CMS-related debugging parameters.
To add new parameters, right-click
Initialization Parameters in the left pane of the
Application Assembly Tool window and select New.
This displays the New Initialization Parameter window.
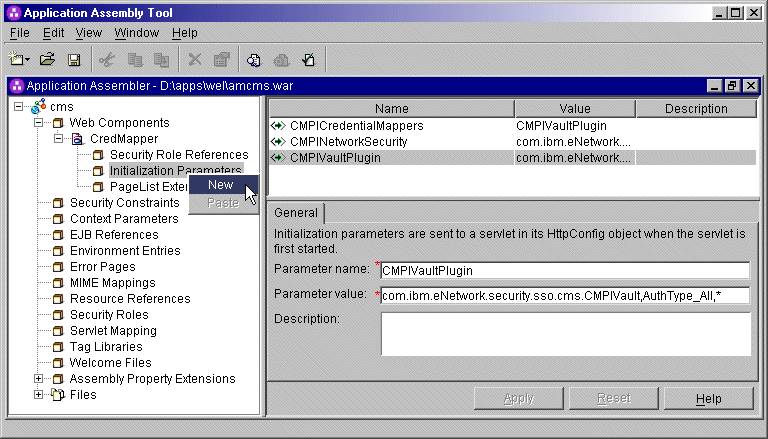
Add the following two optional debugging parameters to help you troubleshoot:
<init-param>
<param-name>CMPI_TRACE_LOG_FILE</param-name>
<param-value>C:\Program Files\IBM\HostOnDemand\HOD\HODWEL.log</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>CMPI_CMS_TRACE_LEVEL</param-name>
<param-value>3</param-value>
</init-param>4. Add the required Vault parameters for the CMPIVaultPlugin.
Adding the required Vault parameters allows the HCM to map the users' network IDs to their host IDs and receive the needed passwords from the vault-style database. The following Vault parameters are required in order for Web Express Logon to function properly. This section is divided into two subsections, A and B.
A. The following parameters contain all the relevant information needed to connect to your HCM, which in this case is a JDBC database table created with IBM DB2. You can either configure access to an existing database or to a newly created one.
B. The following parameters correspond directly to the column headings that you added to your HCM database table in Step 3: Create the Host Credential Mapper database. Recall that you added the following five column headings, all in uppercase: NETWORKID, HOSTADDRESS, APPLICATIONID, HOSTID, and PASSWORD.
The level of security for the database depends on the database vendor. See the documentation for details.
- CMPI_VAULT_DB_ADDRESS
- This is a URL string that provides the address of the database. An example of this string is jdbc:db2://dtagw.raleigh.ibm.com:6789/HODSSO.
Code example:
<init-param>
<param-name>CMPI_VAULT_DB_ADDRESS</param-name>
<param-value>jdbc:db2://dtagw.raleigh.ibm.com:6789/HODSSO</param-value>
</init-param>
CMPI_VAULT_DB_NET_DRIVER- This string contains the name of the class that acts as the network database driver. An example of this string is COM.ibm.db2.jdbc.net.DB2Driver. The location of this class is assumed to be in the existing class path.
Code example:
<init-param>
<param-name>CMPI_VAULT_DB_NET_DRIVER</param-name>
<param-value>COM.ibm.db2.jdbc.net.DB2Driver</param-value>
</init-param>
CMPI_VAULT_DB_USERID- This is the ID of the user account to use when accessing the database. In this case, the user ID is
admin.
Code example:
<init-param>
<param-name>CMPI_VAULT_DB_USERID</param-name>
<param-value>admin</param-value>
</init-param>
CMPI_VAULT_DB_PASSWORD- This is the password of the user account to use when accessing the database.
We strongly recommend that you encrypt this parameter using the password encryption tool provided with Host On-Demand. The tool encrypts the password and then decrypts it so the HCM plug-in can use it. To learn more about how to use this tool, refer to Using the Password Encryption Tool.
Example:
<init-param>
<param-name>CMPI_VAULT_DB_PASSWORD</param-name>
<param-value>tuBu9v81HiJiljt08UgHzA==</param-value>
</init-param>
CMPI_VAULT_DB_TABLE- This identifies the table to use for the needed query. In this case, the table is called
HACP.
Example:
<init-param>
<param-name>CMPI_VAULT_DB_TABLE</param-name>
<param-value>HACP</param-value>
</init-param>
The APPLICATIONID column is not required for FTP sessions.
Based on the information provided by the first three of these parameters (network ID, host address, and the host application ID), you can make a SQL query of the database to get the host ID. The result of the query is entered in the host ID (HOSTID) column. Assuming that the query is successful, a call is made to the vault-style database to request the password.
- CMPI_VAULT_DB_NETID_COL_NAME
- This entry identifies the name of the column that contains the network ID value (NETWORKID).
Code example:
<init-param>
<param-name>CMPI_VAULT_DB_NETID_COL_NAME</param-name>
<param-value>NETWORKID</param-value>
</init-param>
CMPI_VAULT_DB_HOSTADDR_COL_NAME- This entry identifies the name of the column that contains the host address value (HOSTADDRESS).
Code example:
<init-param>
<param-name>CMPI_VAULT_DB_HOSTADDR_COL_NAME</param-name>
<param-value>HOSTADDRESS</param-value>
</init-param>
CMPI_VAULT_DB_HOSTAPP_COL_NAME- This entry identifies the name of the column that contains the host application value (APPLICATIONID).
Code example:
<init-param>
<param-name>CMPI_VAULT_DB_HOSTAPP_COL_NAME</param-name>
<param-value>APPLICATIONID</param-value>
</init-param>
CMPI_VAULT_DB_HOSTID_COL_NAME- This entry identifies the name of the column that contains the host ID value (HOSTID).
Code example:
<init-param>
<param-name>CMPI_VAULT_DB_HOSTID_COL_NAME</param-name>
<param-value>HOSTID</param-value>
</init-param>
- CMPI_VAULT_DB_HOSTPW_COL_NAME
- This entry identifies the name of the column that contains the host password value (PASSWORD).
Code example:
<init-param>
<param-name>CMPI_VAULT_DB_HOSTPW_COL_NAME</param-name>
<param-value>PASSWORD</param-value>
</init-param>
5. Add optional Vault parameters (if desired).
Unlike the previous set of Vault parameters, the following parameters are optional. Which of these parameters you add to the web.xml file depends on your environment and your objectives as an administrator:
<init-param>
<param-name>CMPI_VAULT_TRACE_LEVEL</param-name>
<param-value>3</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>CMPI_VAULT_DB_PRESERVE_WHITESPACE</param-name>
<param-value>false</param-value>
</init-param>On the Application Assembly Tool window, click File > Save to save your WAR file. If it saves successfully, this window will appear as a confirmation:
Click Next to deploy the CMS.