User's Guide and Reference
DB2 Spatial Extender has several functions that generate geometries from ESRI
shape representations. In addition to the two-dimensional
representation supported by the open GIS well-known binary representation, the
ESRI shape representation also supports optional Z coordinates and
measures. The following functions generate geometry from an ESRI
shape:
- ST_GeometryFromShape
- Creates a geometry from a shape representation of any geometry
type.
- ST_PointFromShape
- Creates a point from a point shape representation.
- ST_LineFromShape
- Creates a linestring from a linestring shape representation.
- ST_PolyFromShape
- Creates a polygon from a polygon shape representation.
- ST_MPointFromShape
- Creates a multipoint from a multipoint shape representation.
- ST_MLineFromShape
- Creates a multilinestring from a multilinestring shape
representation.
- ST_MPolyFromShape
- Creates a multipolygon from a multipolygon shape representation.
The general syntax of these functions is the same. The first
argument is the shape representation entered as a binary large object
(BLOB) data type. The second argument is the spatial
reference identifier integer to assign to the geometry. The
GeometryFromShape function has the following syntax:
db2gse.GeometryFromShape(ShapeGeometry Blob(1M), cr db2gse.coordref)
Because these shape functions require the definition of C programming
language structures to map the binary representation, they are intended for
use within a 3GL program and are not suited to a 4GL environment. The
AsShape function converts the geometry value into an ESRI shape
representation.
A shape type of 0 indicates a null shape, with no geometric data for the
shape.
| Value
| Shape Type
|
| 0
| Null Shape
|
| 1
| Point
|
| 3*
| PolyLine
|
| 5
| Polygon
|
| 8
| MultiPoint
|
| 11
| PointZ
|
| 13
| PolyLineZ
|
| 15
| PolygonZ
|
| 18
| MultiPointZ
|
| 21
| PointM
|
| 23
| PolyLineM
|
| 25
| PolygonM
|
| 28
| MultiPointM
|
| Note: | * Shape types that are not specified above (2, 4, 6, and so
forth) are reserved for future use.
|
A point consists of a pair of double precision coordinates in the order
X, Y.
Table 66.
Point byte stream contents
|
Position
|
Field
|
Value
|
Type
|
Number
|
Order
|
|
Byte 0
|
Shape Type
|
1
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 4
|
X
|
X
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 12
|
Y
|
Y
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
A MultiPoint consists of a collection of points. The bounding
box is stored in the order Xmin, Ymin, Xmax, Ymax.
Table 67.
MultiPoint byte stream contents
|
Position
|
Field
|
Value
|
Type
|
Number
|
Order
|
|
Byte 0
|
Shape Type
|
8
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 4
|
Box
|
Box
|
Double
|
4
|
Little
|
|
Byte 36
|
NumPoints
|
NumPoints
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 40
|
Points
|
Points
|
Point
|
NumPoints
|
Little
|
A PolyLine is an ordered set of vertices that consists of one or more
parts. A part is a connected sequence of two or more points.
Points might or might not be connected to each other. Parts might or
might not intersect each other.
Because this specification does not forbid consecutive points with
identical coordinates, shapefile readers must handle such cases. On the
other hand, the degenerate, zero length parts that might result are not
allowed.
The fields for a PolyLine are:
- Box
- The bounding box for the PolyLine stored in the order Xmin, Ymin, Xmax,
Ymax.
- NumParts
- The number of parts in the PolyLine.
- NumPoints
- The total number of points for all parts.
- Parts
- An array of length NumParts. Each PolyLine stores the index of its
first point in the points array. Array indexes are with respect to
0.
- Points
- An array of length NumPoints. The points for each part in the
PolyLine are stored end to end. The points for part 2 follow the points
for part 1, and so on. The parts array holds the array index of the
starting point for each part. There is no delimiter in the points array
between parts.
Table 68.
PolyLine byte stream contents
|
Position
|
Field
|
Value
|
Type
|
Number
|
Order
|
|
Byte 0
|
Shape Type
|
3
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 4
|
Box
|
Box
|
Double
|
4
|
Little
|
|
Byte 36
|
NumParts
|
NumParts
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 40
|
NumPoints
|
NumPoints
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 44
|
Parts
|
Parts
|
Integer
|
NumParts
|
Little
|
|
Byte X
|
Points
|
Points
|
Point
|
NumPoints
|
Little
|
| Note: | X = 44 + 4 * NumParts.
|
A polygon consists of one or more rings. A ring is a connected
sequence of four or more points that forms a closed, non-self-intersecting
loop. A polygon can contain multiple outer rings. The order of
vertices or orientation for a ring indicates which side of the ring is the
interior of the polygon. The neighborhood to the right of an observer
walking along the ring in vertex order is the neighborhood inside the
polygon. Vertices of rings that define holes in polygons are in a
counter-clockwise direction. Vertices for a single, ringed polygon are,
therefore, always in clockwise order. The rings of a polygon are called
parts.
Because this specification does not forbid consecutive points with
identical coordinates, shapefile readers must handle such cases. On the
other hand, the degenerate, zero length, or zero area parts that might result
are not allowed.
The fields for a polygon are:
- Box
- The bounding box for the polygon stored in the order Xmin, Ymin, Xmax,
Ymax.
- NumParts
- The number of rings in the polygon.
- NumPoints
- The total number of points for all rings.
- Parts
- An array of length NumParts. Stores, for each ring, the index of
its first point in the points array. Array indexes are with respect to
0.
- Points
- An array of length NumPoints. The points for each ring in the
polygon are stored end to end. The points for Ring 2 follow the points
for Ring 1, and so on. The parts array holds the array index of the
starting point for each ring. There is no delimiter in the points array
between rings.
- Important notes about Polygon shapes:
-
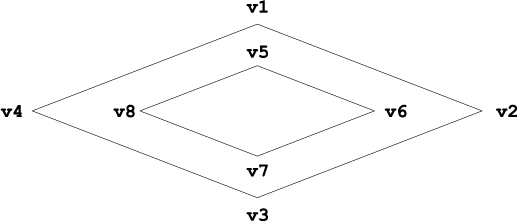
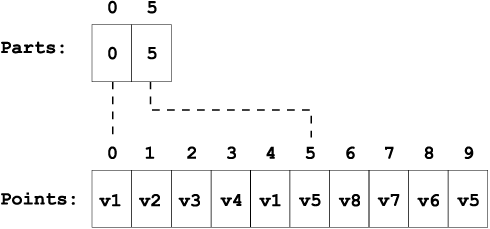
Figure 40. A polygon with a hole and eight vertices
Figure 41. Contents of the polygon byte stream. NumParts equals 2 and NumPoints equals 10. Note that the order of the points for the donut (hole) polygon are reversed.
Table 69.
Polygon byte stream contents
|
Position
|
Field
|
Value
|
Type
|
Number
|
Order
|
|
Byte 0
|
Shape Type
|
5
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 4
|
Box
|
Box
|
Double
|
4
|
Little
|
|
Byte 36
|
NumParts
|
NumParts
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 40
|
NumPoints
|
NumPoints
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 44
|
Parts
|
Parts
|
Integer
|
NumParts
|
Little
|
|
Byte X
|
Points
|
Points
|
Point
|
NumPoints
|
Little
|
| Note: | X = 44 + 4 * NumParts.
|
A PointM consists of a pair of double precision coordinates in the
order X, Y, plus a measure M.
Table 70.
PointM byte stream contents
|
Position
|
Field
|
Value
|
Type
|
Number
|
Order
|
|
Byte 0
|
Shape Type
|
21
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 4
|
X
|
X
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 12
|
Y
|
Y
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 20
|
M
|
M
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
The fields for a MultiPointM are:
- Box
- The bounding box for the MultiPointM stored in the order Xmin, Ymin, Xmax,
Ymax.
- NumPoints
- The number of Points.
- Points
- An array of Points of length NumPoints.
- NumMs
- The number of Measures that follow. NumMs can only have two values
zero if no Measures follow this field; or equal to NumPoints if Measures
are present.
- M Range
- The minimum and maximum measures for the MultiPointM stored in the order
Mmin, Mmax.
- M Array
- An array of Measures of length NumPoints.
Table 71.
MultiPointM byte stream contents
|
Position
|
Field
|
Value
|
Type
|
Number
|
Order
|
|
Byte 0
|
Shape Type
|
28
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 4
|
Box
|
Box
|
Double
|
4
|
Little
|
|
Byte 36
|
NumPoints
|
NumPoints
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 40
|
Points
|
Points
|
Point
|
NumPoints
|
Little
|
|
Byte X
|
NumMs
|
NumMs
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte X+4*
|
Mmin
|
Mmin
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte X+12*
|
Mmax
|
Mmax
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte X+20*
|
Marray
|
Marray
|
Double
|
NumPoints
|
Little
|
Notes:
- X = 40 + (16 * NumPoints)
- * optional
A shapefile PolyLineM consists of one or more parts. A part is a
connected sequence of two or more points. Parts might or might not be
connected to each other. Parts might or might not intersect one
another.
The fields for a PolyLineM are:
- Box
- The bounding box for the PolyLineM stored in the order Xmin, Ymin, Xmax,
Ymax.
- NumParts
- The number of parts in the PolyLineM.
- NumPoints
- The total number of points for all parts.
- Parts
- An array of length NumParts. Stores, for each part, the index of
its first point in the points array. Array indexes are with respect to
0.
- Points
- An array of length NumPoints. The points for each part in the
PolyLineM are stored end to end. The points for part 2 follow the
points for part 1, and so on. The parts array holds the array index of
the starting point for each part. There is no delimiter in the points
array between parts.
- NumMs
- The number of Measures that follow. NumMs can only have two values
zero if no Measures follow this field; or equal to NumPoints if Measures
are present.
- M Range
- The minimum and maximum measures for the PolyLineM stored in the order
Mmin, Mmax.
- M Array
- An array of length NumPoints. The measures for each part in the
PolyLineM are stored end to end. The measures for part 2 follow the
measures for part 1, and so on. The parts array holds the array index
of the starting point for each part. There is no delimiter in the
measure array between parts.
Table 72.
PolyLineM byte stream contents
|
Position
|
Field
|
Value
|
Type
|
Number
|
Order
|
|
Byte 0
|
Shape Type
|
13
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 4
|
Box
|
Box
|
Double
|
4
|
Little
|
|
Byte 36
|
NumParts
|
NumParts
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 40
|
NumPoints
|
NumPoints
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 44
|
Parts
|
Parts
|
Integer
|
NumParts
|
Little
|
|
Byte X
|
Points
|
Points
|
Point
|
NumPoints
|
Little
|
|
Byte Y
|
NumMs
|
NumMs
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte Y+4*
|
Mmin
|
Mmin
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte Y+12*
|
Mmax
|
Mmax
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte Y+20*
|
Marray
|
Marray
|
Double
|
NumPoints
|
Little
|
Notes:
- X = 44 + (4 * NumParts), Y = X
+ (16 * NumPoints).
- * optional
A PolygonM consists of a number of rings. A ring is a closed,
non-self-intersecting loop. Note that intersections are calculated in
XY space, not in XYM space. A PolygonM can contain multiple
outer rings. The rings of a PolygonM are called parts.
The fields for a PolygonM are:
- Box
- The bounding box for the PolygonM stored in the order Xmin, Ymin, Xmax,
Ymax.
- NumParts
- The number of rings in the PolygonM.
- NumPoints
- The total number of points for all rings.
- Parts
- An array of length NumParts. Stores, for each ring, the index of
its first point in the points array. Array indexes are with respect to
0.
- Points
- An array of length NumPoints. The points for each ring in the
PolygonM are stored end to end. The points for Ring 2 follow the points
for Ring 1, and so on. The parts array holds the array index of the
starting point for each ring. There is no delimiter in the points array
between rings.
- NumMs
- The number of Measures that follow. NumMs can have only two zero
values if no Measures follow this field, or equal to NumPoints if Measures are
present.
- M Range
- The minimum and maximum measures for the PolygonM stored in the order
Mmin, Mmax.
- M Array
- An array of length NumPoints. The measures for each ring in the
PolygonM are stored end to end. The measures for Ring 2 follow the
measures for Ring 1, and so on. The parts array holds the array index
of the starting measure for each ring. There is no delimiter in the
measure array between rings.
- Important notes about PolygonM shapes:
-
- The rings are closed (the first and last vertex of a ring must be
the same).
- The order of rings in the points array is not significant.
Table 73.
PolygonM byte stream contents
|
Position
|
Field
|
Value
|
Type
|
Number
|
Order
|
|
Byte 0
|
Shape Type
|
15
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 4
|
Box
|
Box
|
Double
|
4
|
Little
|
|
Byte 36
|
NumParts
|
NumParts
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 40
|
NumPoints
|
NumPoints
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 44
|
Parts
|
Parts
|
Integer
|
NumParts
|
Little
|
|
Byte X
|
Points
|
Points
|
Point
|
NumPoints
|
Little
|
|
Byte Y
|
NumMs
|
NumMs
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte Y+4*
|
Mmin
|
Mmin
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte Y+12*
|
Mmax
|
Mmax
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte Y+20*
|
Marray
|
Marray
|
Double
|
NumPoints
|
Little
|
Notes:
- X = 44 + (4 * NumParts), Y = X
+ (16 * NumPoints).
- * optional
A PointZ consists of triplet, double precision coordinates in the order
X, Y, Z plus a measure.
Table 74.
PointZ byte stream contents
|
Position
|
Field
|
Value
|
Type
|
Number
|
Order
|
|
Byte 0
|
Shape Type
|
11
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 4
|
X
|
X
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 12
|
Y
|
Y
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 20
|
Z
|
Z
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 28
|
Measure
|
M
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
A MultiPointZ represents a set of PointZs, as follows:
- The bounding box is stored in the order Xmin, Ymin, Xmax, Ymax.
- The bounding Z range is stored in the order Zmin, Zmax. Bounding M
Range is stored in the order Mmin, Mmax.
Table 75.
MultiPointZ byte stream contents
|
Position
|
Field
|
Value
|
Type
|
Number
|
Order
|
|
Byte 0
|
Shape Type
|
18
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 4
|
Box
|
Box
|
Double
|
4
|
Little
|
|
Byte 36
|
NumPoints
|
NumPoints
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 40
|
Points
|
Points
|
Point
|
NumPoints
|
Little
|
|
Byte X
|
Zmin
|
Zmin
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte X+8
|
Zmax
|
Zmax
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte X+16
|
Zarray
|
Zarray
|
Double
|
NumPoints
|
Little
|
|
Byte Y
|
NumMs
|
NumMs
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte Y+4*
|
Mmin
|
Mmin
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte Y+12*
|
Mmax
|
Mmax
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte Y+20*
|
Marray
|
Marray
|
Double
|
NumPoints
|
Little
|
Notes:
- X = 40 + (16 * NumPoints); Y
= X + 16 + (8 * NumPoints)
- * optional
A PolyLineZ consists of one or more parts. A part is a connected
sequence of two or more points. Parts might or might not be connected
to each other. Parts might or might not intersect one another.
The fields for a PolyLineZ are:
- Box
- The bounding box for the PolyLineZ stored in the order Xmin, Ymin, Xmax,
Ymax.
- NumParts
- The number of parts in the PolyLineZ.
- NumPoints
- The total number of points for all parts.
- Parts
- An array of length NumParts. Stores, for each part, the index of
its first point in the points array. Array indexes are with respect to
0.
- Points
- An array of length NumPoints. The points for each part in the
PolyLineZ are stored end to end. The points for part 2 follow the
points for part 1, and so on. The parts array holds the array index of
the starting point for each part. There is no delimiter in the points
array between parts.
- Z Range
- The minimum and maximum Z values for the PolyLineZ stored in the order
Zmin, Zmax.
- Z Array
- An array of length NumPoints. The Z values for each part in the
PolyLineZ are stored end to end. The Z values for part 2 follow the Z
values for part 1, and so on. The parts array holds the array index of
the starting point for each part. There is no delimiter in the Z array
between parts.
- NumMs
- The number of Measures that follow. NumMs can only have two values
zero if no Measures follow this field; or equal to NumPoints if Measures
are present.
- M Range
- The minimum and maximum measures for the PolyLineZ stored in the order
Mmin, Mmax.
- M Array
- An array of length NumPoints. The measures for each part in the
PolyLineZ are stored end to end. The measures for part 2 follow the
measures for part 1, and so on. The parts array holds the array index
of the starting measure for each part. There is no delimiter in the
measure array between parts.
Table 76.
PolyLineZ byte stream contents
|
Position
|
Field
|
Value
|
Type
|
Number
|
Order
|
|
Byte 0
|
Shape Type
|
13
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 4
|
Box
|
Box
|
Double
|
4
|
Little
|
|
Byte 36
|
NumParts
|
NumParts
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 40
|
NumPoints
|
NumPoints
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 44
|
Parts
|
Parts
|
Integer
|
NumParts
|
Little
|
|
Byte X
|
Points
|
Points
|
Point
|
NumPoints
|
Little
|
|
Byte Y
|
Zmin
|
Zmin
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte Y+8
|
Zmax
|
Zmax
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte Y+16
|
Zarray
|
Zarray
|
Double
|
NumPoints
|
Little
|
|
Byte Z
|
NumMs
|
NumMs
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte Z+4*
|
Mmin
|
Mmin
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte Z+12*
|
Mmax
|
Mmax
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte Z+20*
|
Marray
|
Marray
|
Double
|
NumPoints
|
Little
|
Notes:
- X = 44 + (4 * NumParts), Y = X
+ (16 * NumPoints), Z = Y + 16 +
(8 * NumPoints)
- * optional
A PolygonZ consists of a number of rings. A ring is a closed,
non-self-intersecting loop. A PolygonZ can contain multiple outer
rings. The rings of a PolygonZ are called parts.
The fields for a PolygonZ are:
- Box
- The bounding box for the PolygonZ stored in the order Xmin, Ymin, Xmax,
Ymax.
- NumParts
- The number of rings in the PolygonZ.
- NumPoints
- The total number of points for all rings.
- Parts
- An array of length NumParts. Stores, for each ring, the index of
its first point in the points array. Array indexes are with respect to
0.
- Points
- An array of length NumPoints. The points for each ring in the
PolygonZ are stored end to end. The points for Ring 2 follow the points
for Ring 1, and so on. The parts array holds the array index of the
starting point for each ring. There is no delimiter in the points array
between rings.
- Z Range
- The minimum and maximum Z values for the arc stored in the order Zmin,
Zmax.
- Z Array
- An array of length NumPoints. The Z values for each ring in the
PolygonZ are stored end to end. The Z values for Ring 2 follow the Z
values for Ring 1, and so on. The parts array holds the array index of
the starting Z value for each ring. There is no delimiter in the Z
value array between rings.
- NumMs
- The number of Measures that follow. NumMs can only have two values
zero if no Measures follow this field; or equal to NumPoints if Measures
are present.
- M Range
- The minimum and maximum measures for the PolygonZ stored in the order
Mmin, Mmax.
- M Array
- An array of length NumPoints. The measures for each ring in the
PolygonZ are stored end to end. The measures for Ring 2 follow the
measures for Ring 1, and so on. The parts array holds the array index
of the starting measure for each ring. There is no delimiter in the
measure array between rings.
- Important notes about PolygonZ shapes:
-
- The rings are closed (the first and last vertex of a ring MUST be
the same).
- The order of rings in the points array is not significant.
Table 77.
PolygonZ byte stream contents
|
Position
|
Field
|
Value
|
Type
|
Number
|
Order
|
|
Byte 0
|
Shape Type
|
15
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 4
|
Box
|
Box
|
Double
|
4
|
Little
|
|
Byte 36
|
NumParts
|
NumParts
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 40
|
NumPoints
|
NumPoints
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte 44
|
Parts
|
Parts
|
Integer
|
NumParts
|
Little
|
|
Byte X
|
Points
|
Points
|
Point
|
NumPoints
|
Little
|
|
Byte Y
|
Zmin
|
Zmin
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte Y+8
|
Zmax
|
Zmax
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte Y+16
|
Zarray
|
Zarray
|
Double
|
NumPoints
|
Little
|
|
Byte Z
|
NumMs
|
NumMs
|
Integer
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte Z+4*
|
Mmin
|
Mmin
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte Z+12*
|
Mmax
|
Mmax
|
Double
|
1
|
Little
|
|
Byte Z+20*
|
Marray
|
Marray
|
Double
|
NumPoints
|
Little
|
[ Top of Page | Previous Page | Next Page ]