When using DB2 Universal Database Enterprise - Extended Edition, you may be working in a communication-intensive environment where overall system throughput is vital to your business.
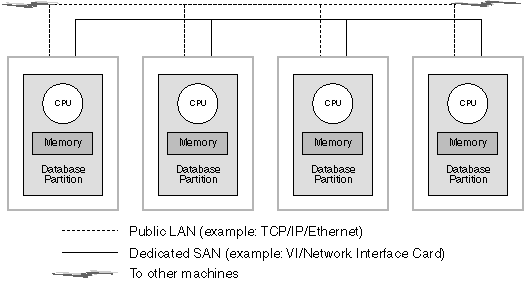
There are two types of networks that may be used for your massively parallel processing (MPP) environment. One uses TCP/IP over a public LAN. The other type uses TCP/IP or the Virtual Interface (VI) architecture over a dedicated interconnect.
The public interconnect works with existing TCP/IP. TCP/IP is available as a communication protocol almost everywhere. This is a Local Area Network (LAN) environment. An advantage with this environment is that you can choose to immediately attach your cluster without requiring additional proprietary hardware and software. A disadvantage with this environment is that the additional cluster traffic affects the quality of the service over the entire LAN. For example, there could be a communication "burst" effect with database activity within the cluster that affects communication across the LAN. Also, the communications of the rest of the LAN environment makes it difficult to maintain consistent performance of database processing within the cluster.
The dedicated interconnect works as a separate network. The network may be the only network available for use within the cluster or it may be used in addition to the LAN environment. The network is dedicated to providing communications between the members of the cluster. This is called a System Area Network (SAN). Performance of the database is not affected by external communications traffic (as in a LAN environment), and the reverse is also true. A disadvantage with this environment is that there may be separate administration required for both networks as well as additional separate hardware, software, and protocol costs for both the LAN and the SAN. An example of a dedicated interconnect is the 100 Mb/Sec Ethernet.
You may wish to maintain your pre-existing public LAN environment, but you also want the ability to bulk transfer data over the SAN (within your cluster). Such an arrangement is convenient if you want to have communication access beyond the cluster. Within a Windows NT operating environment, you may need to retain the public LAN for communication access to the NT Domain Controller. (See Appendix L, How DB2 for Windows NT Works with Windows NT Security for information on the Domain Controller.)
Figure 125. Combine dedicated SAN with public LAN
 |
The remaining sections include discussions of: