DB2 Connect implements the DRDA architecture to reduce the cost and complexity of accessing data stored in DB2 Universal Database for AS/400, DB2 Universal Database for OS/390, DB2 for MVS/ESA, DB2 for VSE & VM, and other DRDA-compliant database servers. By fully exploiting the DRDA architecture, DB2 Connect offers a well-performing, low-cost solution with the system management characteristics that customers demand.
In DRDA terminology, an application requester (AR) is the code that handles the application end of a distributed connection; it is the application that is requesting data. An application server (AS) is the code that handles the database end of the connection. In the DB2 Connect environment, the DB2 Connect workstation can only function as an application requester on behalf of application programs.
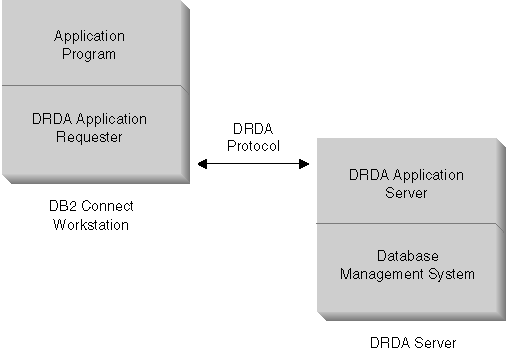
Figure 1 shows the flow of data between the DB2 Connect workstation and the DRDA server in the case where there are local clients only. In addition, a private protocol exists between the DB2 Connect workstation and any remote clients.
Figure 1. Data Flow Between a DB2 Connect Workstation and a DRDA Server
 |
To implement the connections between DRDA server database management systems and database clients, DRDA uses the following architectures:
These architectures used as building blocks. The data streams which flow over the network are specified by DRDA architecture, which documents a data stream protocol supporting distributed relational database access.
A request is routed to the correct destination by means of directories that contain various types of communication information and the name of the DRDA server database being accessed.