DB2 supports multiple database manager instances on the same machine. A database manager instance has its own configuration files, directories, and databases.
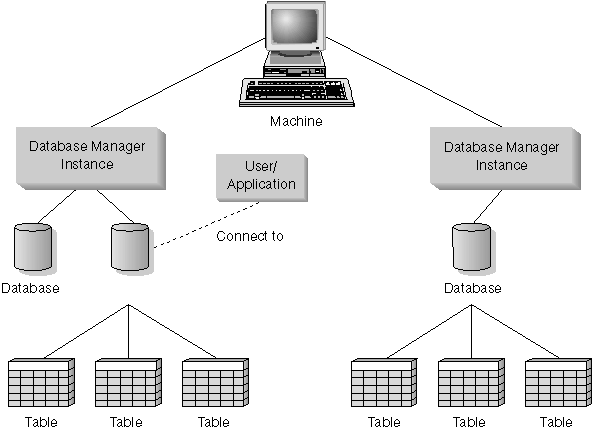
Each database manager instance can manage several databases. However, a given database belongs to only one instance. Figure 1 shows this relationship.
Figure 1. Database Manager Instances

Database manager instances give you the flexibility to have multiple database environments on the same machine. For example, you can have one database manager instance for development, and another instance for production.
With UNIX servers you can have different DB2 versions on different database manager instances. For example, you can have one database manager instance running DB2 Universal Database Version 6.1, and another running DB2 Universal Database Version 7.1. However, within a version level, only one release and modification level are supported. For example, DB2 Version 5.0 and DB2 Version 5.2 cannot coexist on a UNIX server.
With OS/2, Windows NT and Windows 2000 servers, you must have the same DB2 version, release, and modification level on each database manager instance. You cannot have one database manager instance running DB2 Universal Database Version 6.1, and another instance running DB2 Universal Database Version 7.1.
You need to know the following for each instance you use:
For OS/2, Windows NT and Windows 2000, this is an alphanumeric string of up to eight characters. An instance named "DB2" is created for you during install.
For UNIX platforms, the instance directory is $HOME/sqllib, where $HOME is the home directory of the instance owner.
For OS/2, Windows NT and Windows 2000, the instance directory is %DB2PATH%\instance_name. The variable %DB2PATH% determines where DB2 is installed. Depending on which drive DB2 is installed, %DB2PATH% will point to drive:\sqllib.
The instance path on OS/2, Windows NT and Windows 2000 is created based on either:
%DB2PATH%\%DB2INSTANCE% (for example, C:\SQLLIB\DB2)
or, if DB2INSTPROF is defined:
%DB2INSTPROF%\%DB2INSTANCE% (for example, C:\PROFILES\DB2)
The DB2INSTPROF environment variable is used on OS/2, Windows NT and Windows 2000 to support running DB2 on a network drive in which the client machine has only read access. In this case, DB2 will be set to point to drive:\sqllib, and DB2INSTPROF will be set to point to a local path (for example, C:\PROFILES) which will contain all instance specific information such as catalogs and configurations, since DB2 requires update access to these files.
For information about creating and managing database manager instances, refer to the Quick Beginnings book for your platform.