Installation and Configuration Supplement
To access a remote server through APPC, you must first
have installed and configured communication software on both the client and
server workstations. This section describes how to set up APPC
communications for inbound client connections on a DB2 Connect or DB2
Universal Database server. These connections can be from workstations
running DB2 clients, host database clients, or AS/400 database clients.
See Software Requirements for the communication protocol requirements for your
platform. See Possible Client-to-Server Connectivity Scenarios for the supported communication protocols for your
particular client and server.
Before completing the steps in this section, be sure that you have
completed the instructions in Setting the DB2COMM Registry Parameter.
The following steps are required to set up APPC communications:
step 1.
| Identify and record parameter values.
|
step 2.
| Configure the server:
- Update the database manager configuration file.
- Configure the APPC communications subsystem.
|
Before you configure the server, fill in copies of the worksheet in Table 22.
After you fill in the Your Value entries, you can use the
worksheet to configure APPC communications for inbound connections.
During the configuration process, replace the sample values that appear in the
configuration instructions with your values from the worksheet, using the
boxed numbers (for example, (1)) to relate the configuration
instructions to the worksheet values.
| The worksheet and configuration instructions supply suggested or sample
values for required configuration parameters. For other parameters, use
the communications program's default values. If your network
configuration is different from that used in the instructions, consult your
Network Administrator for values that are appropriate to your network.
|
Table 22. APPC Values Required at the Server
| Ref. #
| Name on the Server
| Sample Value
| Your Value
|
| (1)
| Network ID
| SPIFNET
|
|
| (2)
| Local Control Point Name
| NYX1GW
|
|
| (3)
| Local node or Node ID
| 071 27509
|
|
| (4)
| Local LU name
| NYX1GW0A
|
|
| (5)
| Local LU alias
| NYX1GW0A
|
|
| (6)
| Mode name
| IBMRDB
|
|
| (7)
| Service TP name
| X'07'6DB
|
|
| (8)
| Application TP name
| DB2DRDA
|
|
For each server that you are connecting to, fill in a copy of the worksheet
as follows:
- For network ID ((1)), determine the network name of the
server workstation.
- Determine the local control point name or control point LU
((2)) to be used for the server workstation. This is usually the
same as the Local node or Physical Unit name for the system.
- For local node or node ID ((3)), determine the
IDBLK and IDNUM of the server workstation. The default value should be
correct, or you can obtain the required values from your Network or System
Administrator.
- Determine the local LU name ((4)) to be used by the
server. If you use a Syncpoint Manager to manage multisite updates
(two-phase commit), the local LU should be the LU used for the SPM. In
this case, that LU cannot also be the Control Point LU.
- For local LU alias ((5)), you usually use the same value
as for the local LU name ((4)).
- For mode name ((6)), usually the default
IBMDRB is sufficient.
- For Service TP name ((7)) and Application TP name ((8)),
choose a name of up to 64 characters, or use the default transaction programs,
X'07'6DB' or and DB2DRDA.
|
You will need to record the following entries from the worksheet so that
they can be used to configure communications and directories for each client
from which you will be accepting connections:
- Network ID ((1))
- Local Control Point name ((2))
- Local LU name ((4))
- Mode name ((6))
- Transaction program name ((7)) or ((8)).
|
The following steps describe how to configure this protocol on the
server. Replace the sample value with your value as recorded on your
worksheet.

|
If you want to use only the default transaction programs for a single DB2
instance, you do not need to configure the tpname database manager
configuration parameter. Skip this step and go to B. Configure the APPC Communications Subsystem.
|
The default transaction program names are DB2DRDA and
X'07'6DB'. To configure a DB2 instance to listen for a TP
other than, or in addition to, the default TPs, you must configure the TP name
in the tpname database manager configuration parameter. You
must also configure a unique TP name if you have multiple instances on the
server.
To update the database manager configuration file with the transaction
program name (8)), perform the following steps:
step 1.
| Log on to the system as a user with System Administrative (SYSADM)
authority. For more information, see Working with the System Administrative Group.
|
step 2.
| For UNIX servers, set up the instance environment and invoke the DB2
command line processor as follows:
- Run db2profile or db2cshrc as follows:
. INSTHOME/sqllib/db2profile (for Bourne or Korn shell)
source INSTHOME/sqllib/db2cshrc (for C shell)
where INSTHOME is the home directory of the instance.
- Start the DB2 command line processor by entering the db2
command.
|
step 3.
| Update the database manager configuration file with the server's
transaction program name (tpname) by entering the following
commands:
update dbm cfg using tpname tpname
db2stop
db2start
For example, if the server's transaction program name is
DB2DRDA, use:
update dbm cfg using tpname DB2DRDA
db2stop
db2start
If you are configuring the Administration Server to use APPC, you must also
update the admin server configuration file. If the Administration
Server's transaction program name is DB2ADMIN, enter the
following command:
update admin configuration using tpname DB2ADMIN
db2admin stop
db2admin start
|
If your server contains multiple instances, each accepting connections
using APPC, then each instance requires a unique TP on which to listen.
Only one of these instances can listen for the default TPs. The
db2servicetpinstance registry variable controls which instance
listens for the default TPs (on OS/2, Windows NT, or AIX). Set this
value to the name of the instance you want to listen for these default
TPs.
For example, to ensure that the instance MYINST listens for
default transaction programs, enter the following command:
db2set DB2SERVICETPINSTANCE=MYINST
Consider the following server configuration:
- Two instances are defined on the server, MYINST1 and
MYINST2.
- For MYINST1, the tpname parameter is set to
MYTP1.
- For MYINST2, the tpname parameter is set to
MYTP2.
- DB2SERVICETPINSTANCE is set to MYINST1.
In this configuration, MYINST1 instance will listen for the
MYTP1 in addition to the default TPs DB2DRDA
and X'X'07'6DB'. The MYINST2 instance will
continue to listen for the MYTP2 TP.
If this registry value is not set and multiple instances are configured to
support APPC connections, then unpredictable results will occur.
To configure your DB2 server to accept remote clients using
APPC, you need to update the APPC communications subsystem to support the
transaction program name that the server will use.

|
Go to the section that provides the APPC inbound client connection
instructions for your operating system:
|
This chapter describes how to configure your IBM
eNetwork Communications Server V5.0.2.4 for AIX (CS/AIX)
to accept inbound APPC client connections. CS/AIX is the only product
supported for this purpose.Before you begin, ensure that your
workstation has CS/AIX installed.
For more information on setting up your environment, refer to the online
help supplied with CS/AIX.
The following assumptions have been made:
- The basic installation of the CS/AIX package has already been
completed.
- DB2 Connect or DB2 Universal Database for AIX has been installed.
- The user is logged on as root.
Use the Your Values entries in the worksheet in Table 22 to complete the steps below.
| DB2 automatically configures CS/AIX with the transaction program
parameters required to accept inbound APPC connections. These
instructions describe the remaining steps required to configure your APPC
communications for inbound connections.
|
To configure CS/AIX to accept inbound APPC connections, perform the
following steps:
step 1.
| Log on to the system as a user with root authority and start
the /usr/bin/X11/xsnaadmin program. The Node window for the
server opens.
|
step 2.
| Define a node
- Select Services->Configure Node Parameters from the menu
bar. The Node Parameters window opens.
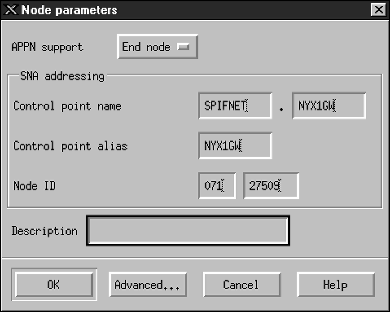
- Click on the APPN support drop down box and select the End
node option.
- Enter your Network ID ((1)) and Control Point name
((2)).
- Enter your Control Point name ((2)) in the Control point
alias fields.
- Enter your Node ID ((3)) in the Node ID fields.
- Click on OK.
|
step 3.
| Define a port
- Select the Connectivity and Dependent LUs window.
- Click on the Add push button. The Add to node window
opens.
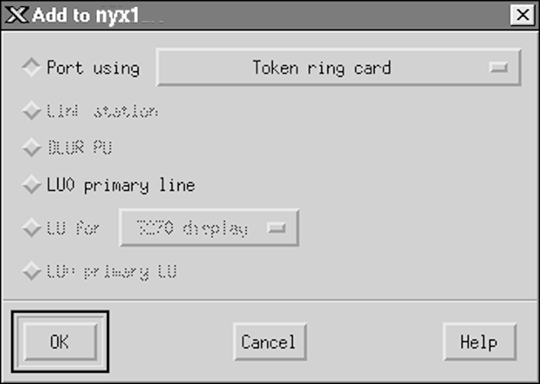
- Select the Port using radio button.
- Click on the Port using drop down box and select the
appropriate port.
| For our example, we will select the Token ring card
option.
|
- Click on OK. The Port window for the chosen port type
opens.
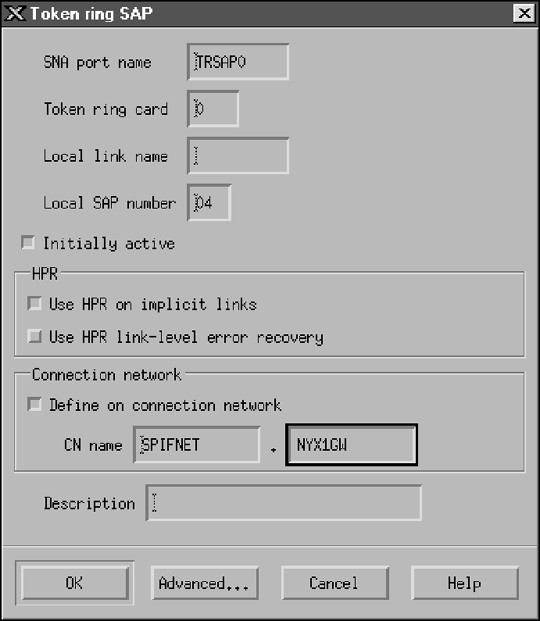
- Enter a name for the port in the SNA port name field.
- Select the Initially active checkbox.
- From the Connection network box, select the Define on a
connection network checkbox.
- Enter your Network ID ((1)) and Control Point name ((2)) in
the CN name fields.
- Click on OK. The Token ring SAP window closes and a new
port appears in the Connectivity and Dependent LUs window.
|
step 4.
| Define a local LU
- Select the Independent local LUs window.
- Click on the Add push button. The Local LU window
opens.
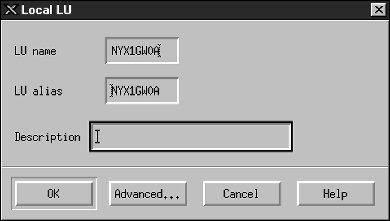
- Enter your independent Local LU name ((4)) in the LU
name field.
- Enter the same name in the LU alias ((5)) field.
- Click on OK. The new LU appears in the Independent
local LUs window.
|
step 5.
| Define a mode
- Select Services->APPC->Modes from the menu bar. The
Modes window opens.
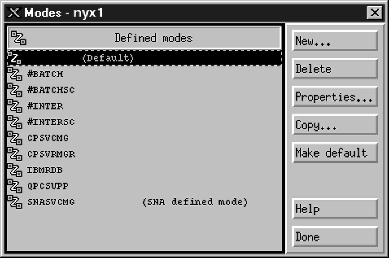
- Click on the New push button. The Mode window
opens.
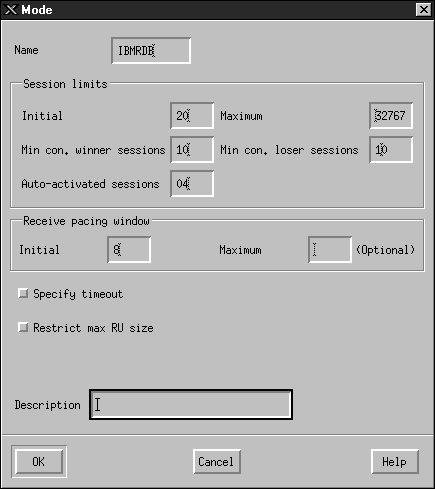
- Enter your Mode name ((6)) in the Name field.
- The configuration values below are suggested for the following
fields:
- Initial Session limits: 20
- Maximum Session limits: 32767
- Min con. winner sessions: 10
- Min con. loser sessions: 10
- Auto-activated session: 4
- Initial Receive pacing window: 8
These values are suggested because they are known to work. You will
need to tailor these values so that they are optimized for your particular
application environment.
- Click on OK. The new mode appears in the Mode
window.
- Click on Done.
|
step 6.
| Close the CS/AIX administration program.
|
step 7.
| Test the APPC connection
- Start the SNA subsystem by entering the /usr/bin/sna start
command. You can enter the /usr/bin/sna stop command to stop
the SNA subsystem first, if required.
- Start the SNA administration program. You can enter either the
/usr/bin/snaadmin command or the /usr/bin/X11/xsnaadmin
command.
- Start the subsystem node. Select the appropriate node icon in the
button bar, and click on the Start button.
|
You have now finished setting up your workstation for inbound APPC
communications.
This section describes how to configure IBM eNetwork
Communications Server for Windows NT V5.01 (CS/NT) to accept inbound
APPC client connections
Before you begin, ensure that the IBM Communications Server for Windows NT
you installed complies with the following restrictions:
__ 1.
| APAR fixes JR11529 and JR11170. These fixes are required to enable
cancelling of queries in progress by using Ctrl-BREAK or issuing the SQLCancel
ODBC/CLI call.
|
__ 2.
| IBM Communications Server IEEE 802.2 LAN interface (this is an
installation option for Communications Server) or LLC2 driver installed from
the IBM Communications Server installation directory. During
installation CS/NT asks if you want to install LLC2. If you are not
sure whether LLC2 was installed with your copy of CS/NT, you can find out as
follows:
step a.
| Click on the Start push button, then select
Settings->Control Panel.
| step b.
| Double-click on the Network icon.
| step c.
| On the Network window, click on the Protocols tab.
IBM LLC2 Protocol must be one of the protocols listed. If it
is not, you need to install this protocol from your IBM Communications Server
for Windows NT software. Refer to its documentation for
instructions.
|
|
For more information on setting up your environment, refer to the online
help supplied with CS/NT, or to the following publications:
- Connectivity Supplement
- DRDA Connectivity Guide
The following assumptions have been made:
- The basic installation of the IBM eNetwork Communication Server
V5.01 for Windows NT package has already been completed.
Use the Your Values entries in the worksheet in Table 22 to complete the steps below.
To configure CS/NT to accept inbound APPC connections, perform the
following steps:
step 1.
| Start IBM Communications Server for Windows NT
- Click Start and select Programs->IBM Communications
Server->SNA Node Configuration. The IBM Communications Server SNA
Node Configuration window opens.
- Select File->New->Advanced.
|
step 2.
| Configure the node
- In the Configuration options box, select Configure
Node, then click on the New push button. The Define
the Node window opens.
- Enter your Network ID ((1)) and local Control Point name
((2)) in the Fully qualified CP name fields.
- Enter the same name in the CP alias field ((2)).
- Enter your Node ID ((3)) in the Local Node ID
field.
- Select the End Node radio button.
- Click on OK.
|
step 3.
| Configure devices
- In the Configuration options field, select Configure
devices.
- Select the appropriate DLC from DLCs field. These
instructions use the LAN DLC.
- Click on the New button. The appropriate window opens
with default values displayed. In this case, the Define a LAN device
window opens.
- Click on OK to accept the default values.
|
step 4.
| Configure the gateway
- In the Configuration options field, select Configure the
Gateway, then click on the New button. The Define
Gateway window opens.
- Select the SNA Clients tab.
- Select the Enable SNA API Client Services check box.
- Click on OK to accept the default values.
|
step 5.
| Configure modes
- In the Configuration options field, select Configure
modes, then click on the New button. The Define a mode
window opens.
- Enter your mode name ((6)) in the Mode name
field.
- Select the Advanced tab.
- Select #CONNECT from the Class of Service Name
field.
- Click on OK.
|
step 6.
| Configure Local LU 6.2
- In the Configuration options field, select Configure local
LU 6.2, then click on the New push button. The
Define a local LU 6.2 window opens.
- Enter your Local LU name ((4)) in the Local LU name
field.
- Enter a value for the LU session limit field. The
default, 0, specifies the maximum allowed value.
- Accept the defaults for the other fields.
- Click on OK.
|
step 7.
| Create a service Transaction Program
- In the Configuration options field, select Configure
Transaction Programs.
- Click on the New push button. The Define a Transaction
Program window opens.
- Select the Basic tab.
- Select the Service TP check box.
- Specify a service TP ((7)) in the TP name field.
- Select the Background Process check box.
- Select the Advanced tab.
- Change the default in the Receive Allocate timeout field to 0
(no timeout).
- If you are configuring Communications Server for use with Communication
Server SNA Client, select the For SNA API Client use check
box.
- Accept the defaults for the other fields.
- Click on OK.
|
step 8.
| Create an Application Transaction Program
- In the Configuration options field, select Configure
Transaction Programs, then click on the New push
button. The Define a Transaction Program window opens.
- Select the Basic tab.
- Clear the the Service TP check box.
- Specify an application TP name ((8)) in the TP name
field.
- Select the Background Process check box.
- Select the Advanced tab.
- Change the default in the Receive Allocate timeout field to 0
(no timeout).
- If you are configuring Communications Server for use with Communication
Server SNA Client, select the For SNA API Client use check
box.
- Accept the defaults for the other fields.
- Click on OK.
|
step 9.
| Save the configuration
- Select File->Save As. The Save As window opens.
- Type in a file name, for example ny3.acg, and click on
OK.
- In the window that opens, you are asked if you want this configuration to
be the default. Click on the Yes button.
|
step 10.
| Update the environment
IBM Communications Server uses an environment variable called
APPCLLU to set the default Local LU used for APPC
communications. You may set this variable on a per-session basis by
opening a command window and entering set
appcllu=local_lu_name, where local_lu_name is the name
of the local LU you want to use. However, you will probably find it
more convenient to permanently set the variable. To permanently set the
variable in Windows NT, perform the following steps:
- Click Start and select Settings->Control
Panel.
- Double-click on the System icon. The System Properties window
opens.
- Select the Environment tab.
- Type APPCLLU in the Variable field.
- Type your local LU name ((4)) in the Value field.
- Click on the Set push button to accept the changes.
- Click on OK to exit the System Properties window.
The environment variable will now remain set for future sessions.
|
step 11.
| Start SNA Node Operations
- Click Start and select Programs->IBM Communication
Server->SNA Node Operations. The SNA Node Operations
window opens.
- Select Operations->Start Node from the menu bar.
- In the window that opens, select the configuration file you saved in the
previous step (for example, ny3.acg) and click on
OK.
|
After installing Communications Server you should register it as a Windows
NT Service. This will automatically start Communications Server when
the machine is booted.
To register Communications Server as an NT service enter the following
command. Either:
csstart -a
to register Communications Server with the default configuration,
or:
csstart -a c:\ibmcs\private\your.acg
where c:\ibmcs\private\your.acg represents the
name of the non-default Communications Server configuration file that you want
to use.
Whenever your machine is booted in the future, Communications Server will
be started automatically with the required configuration file.
|

| Now that you have configured the server, you are ready to install a DB2
client. Go to Installing DB2 Clients for more information.
|
|
This section describes how to configure IBM eNetwork
Communications Server for OS/2 V5 (CS/2) to accept inbound APPC client
connections.
Before you begin, ensure that your workstation has CS/2 V5 or later for
OS/2 installed.
For more information on setting up your environment, refer to the online
help supplied with CS/2, or to the following publications:
- Connectivity Supplement
- DRDA Connectivity Guide
The following assumptions have been made:
- The basic installation of the IBM eNetwork Communication Server V5 for
OS/2 package has already been completed.
- DB2 Connect or DB2 Universal Database for OS/2 has been installed.
Use the Your Values entries in the worksheet in Table 22 to complete the steps below.
| These instructions describe how to create new profiles within a new
configuration. If you are modifying an existing configuration, you may
need to delete some profiles before you can verify the configuration.
|
To configure your system, perform the following steps:
step 1.
| Start a new configuration
- Double-click on the IBM eNetwork Communications Server
icon.
- Double-click on the Communications Manager Setup icon.
- On the Communications Manager Setup panel, click on the Setup
push button.
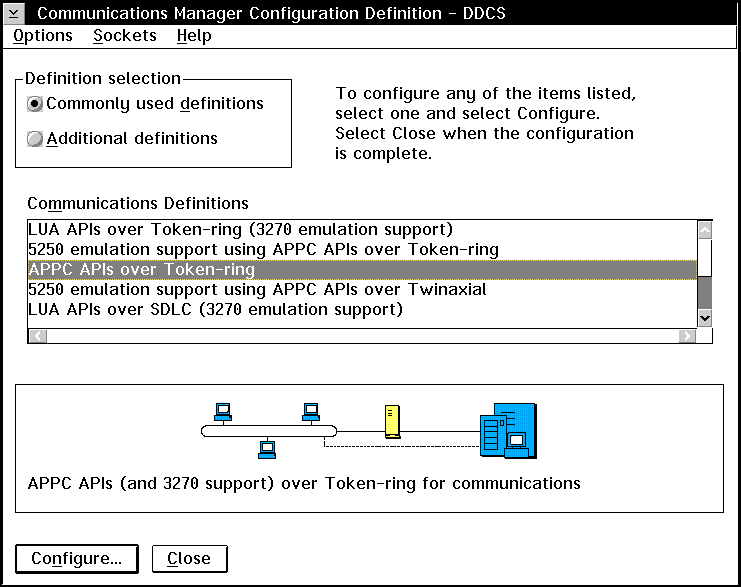
- On the Open Configuration panel, provide a name for a new configuration
file and click on OK. The Communications Manager
Configuration Definition window opens.
|
step 2.
| Configure the protocol
- Select the Commonly used definitions radio button.
- In the Communications Definitions box, select the protocol that you want
to use.
| These intructions use APPC APIs over Token-Ring.
|
- Click on the Configure push button. The APPC APIs over
Token-Ring window opens.
- Enter your Network ID ((1)) and local Control Point name
((2)) in the corresponding fields.
- Click on the End node push button that your network
administrator advises you to use.
|
You can select either the End node - to a network node server
radio button or the End node - no network node server radio
button. A network node server is used when many users are routed
through the same connection. This example assumes no network node
server is used.
|
- Click on the Advanced push button. The Communications
Manager Profile List window opens.
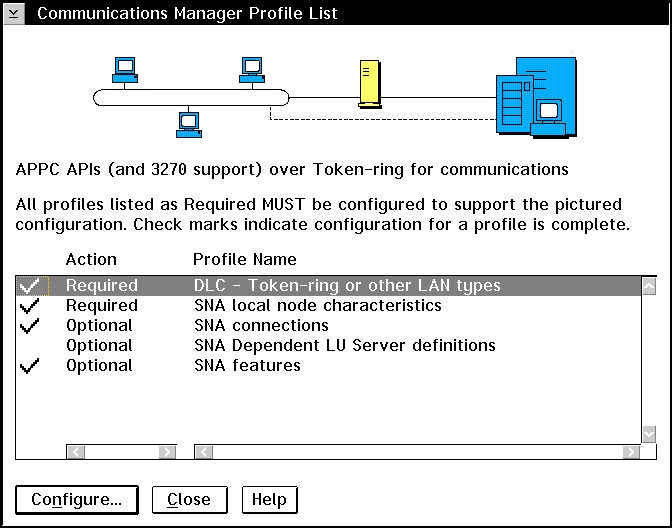
|
Subsequent steps begin from this window. You will return to this
window when each of the following steps are completed.
|
|
step 3.
| Prepare a LAN DLC profile
- On the Profile List window, select the DLC - Token ring or other LAN
Types Adapter Parameters option and click on the Configure
push button. The Token Ring or Other Lan Types Adapter Parameters
window opens.
- Enter your Network ID ((1)) in the Network ID
field.
- Click on OK.
|
step 4.
| Update the SNA local node characteristics
- On the Profile List window, select the SNA local node
characteristics option and click on the Configure push
button. The Local Node Characteristic window opens.
- Enter your Network ID ((1)) in the Network ID
field.
- The Local node name ((2)) was probably set when CS/2 was
installed. If you are not sure, consult your local network
administrator.
- Enter your Node ID ((3)) in the Local node ID (hex)
field.
|
The first part should be filled in for you already when you display the
profile. You only need to complete the second part.
|
- Click on OK.
|
step 5.
| Set SNA features
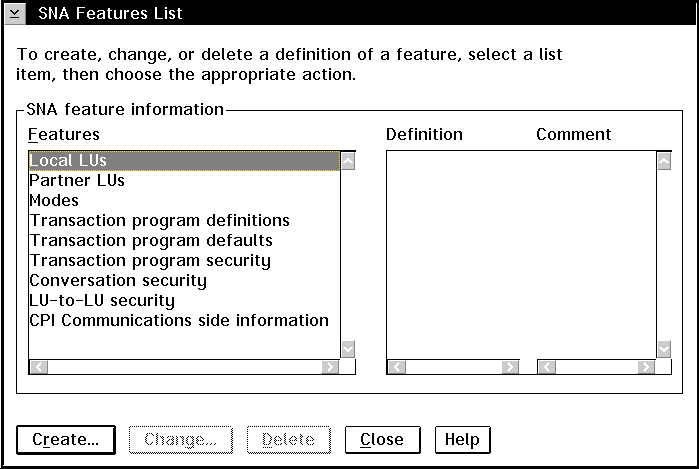
- On the Profile List window, select the SNA features option and
click on the Configure push button. The SNA Features List
window opens. Subsequent steps begin from this window.
|
step 6.
| Prepare a local LU profile
If the DB2 workstation is defined as an independent LU, prepare a Local LU
Profile by performing the following steps:
- On the SNA Features List window, select Local LUs->Create from
the action menu bar.
- Enter your Local LU name ((4)) in the LU name
field.
- Enter your Local LU alias ((5)) in the alias
field.
- Select the Independent LU radio button in the NAU
address box.
- Click on OK.
|
step 7.
| Prepare a mode definition
- From the SNA Features List box, select the Modes option and
click on the Create push button. The Mode Definition window
opens.
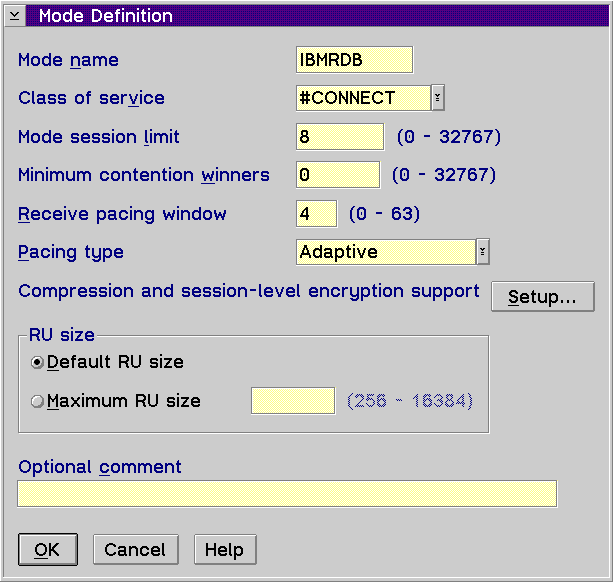
- Enter your Mode name ((6)) in the mode name
field.
- For the other fields, you can either specify values that match the mode
profile defined on your server systems, or tune the parameters.
- Click on OK to finish the creation of the mode and to return to
the SNA Features List panel.
|
step 8.
| Define a transaction program name
- From the SNA Features List panel, double-click on Transaction Program
Definitions. The Transaction Program Definition window
opens.
- Specify your transaction program name ((8)) in the Transaction
program (TP) name field.
- Enter any string, for example, notused, in the OS/2
program path and file name field. This field will not be used to
determine the actual transaction program location, but must be filled to
continue with the configuration steps.
- Select the Conversation security required check box.
- Click on the Continue push button. The Additional TP
Parameters window opens.
- Select the Background radio button from the Presentation
type group.
- Select the Queued, operator preloaded radio button from the
Operation type group.
- Click on OK to finish the TP name definition and return to the
SNA Features List panel.
|
step 9.
| Define conversation security
- From the SNA Features List panel, double-click on
Security. The Conversation Security window opens.
- Select the Utilize User Profile Management check box.
- Click on the Add push button.
- Click on OK to finish the conversation security definition and
return to the SNA Features List panel.
|
step 10.
| Save the configuration
- Click on the Close button to return to the Comminucation Server
Configuration Definition window.
- Click on the Close button to automatically verify and save the
new configuration file, and leave the configuration windows.
- Stop and start Communications Server. Select Stop
Communications Normally->Start Communications.
|
You have now finished setting up your workstation for inbound APPC
communications.
This chapter describes how to configure IBM eNetwork
Personal Communications V4.30 for Windows NT (PCOMM/NT) to accept
inbound APPC client connections.
Before you begin, ensure that the IBM eNetwork Personal Communications
software you installed:
__ 1.
| Is Version 4.30 or higher
|
__ 2.
| Has the LLC2 driver installed from the IBM Communications Server
installation directory. To confirm this, perform the following
steps:
step a.
| Click on the Start push button, then select
Settings->Control Panel.
| step b.
| Double-click on the Network icon. The Network window opens.
| step c.
| On the Network window, click on the Protocols tab.
| step d.
| Verify that IBM LLC2 Protocol is one of the protocols
listed. If it is not, you need to install this protocol from your IBM
Personal Communications for Windows NT software. Refer to its
documentation for instructions.
|
|
For more information on setting up your environment, refer to the online
help supplied with PCOMM/NT or to the following publications:
- IBM DB2 Connectivity Supplement
- DRDA Connectivity Guide
The following assumptions have been made:
- The basic installation of the PCOMM/NT package has already been
completed.
- DB2 Connect or DB2 Universal Database for Windows NT has been
installed.
Use the Your Values entries in the worksheet in Table 22 to complete the steps below.
To start IBM Personal Communications, complete the following steps:
step 1.
| Click Start and select Programs->IBM Communications
Server->SNA Node Configuration. The IBM Personal Communications
SNA Node Configuration window opens.
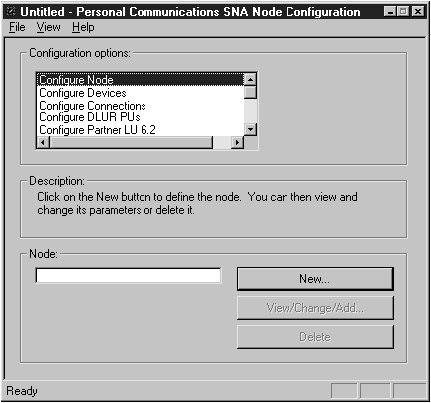
|
step 2.
| Select File->Newfrom the menu bar. The Define the Node
window opens. Subsequent steps will begin from this window.
|
To configure APPC communications, perform the following steps:
step 1.
| Configure the Node
- In the Configuration options box, select Configure
Node, then click on the New push button. The Define
the Node window opens.
- In the Fully qualified CP name fields, type in your Network ID
((1)) and local Control Point name ((2)).
- Optionally, in the CP alias field, type in a CP alias.
If you leave this blank the local control point name ((2)) will be
used.
- Enter your Node ID ((3)) in the Local Node ID
fields.
- Click on OK.
|
step 2.
| Configure the device
- In the Configuration options box, select Configure
devices.
- Select the appropriate DLC from DLCs field. These
instructions use the LAN DLC.
- Click on the New button. The appropriate window opens
with default values displayed. In this case, the Define a LAN device
window opens.
- Click on OK to accept the default values.
|
step 3.
| Configure Modes
- In the Configuration options box, select Configure
modes, then click on the New push button. The Define a
mode window opens.
- Enter your Mode name ((6)) in the Mode name field of the
Basic tab.
- Select the Advanced tab.
- Select #CONNECT from the Class of Service Name
field.
- Click on OK.
|
step 4.
| Configure Local LU 6.2
- In the Configuration options box, select Configure local
LU 6.2, then click on the New button. The
Define a local LU 6.2 window opens.
- Enter your Local LU name ((4)) in the Local LU name
field.
- Type in a value for the LU session limit field. The
default, 0, specifies the maximum allowed value. Accept the
defaults for the other fields.
- Click on OK.
|
step 5.
| Create a service Transaction Program
- In the Configuration options field, select Configure
Transaction Programs.
- Click on the New push button. The Define a Transaction
Program window opens.
- Select the Basic tab.
- Specify a service TP ((7)) in the TP name field.
- Select the Advanced tab.
- Change the default in the Receive Allocate timeout field to 0
(no timeout).
- Accept the defaults for the other fields.
- Click on OK.
|
step 6.
| Create an Application Transaction Program
- In the Configuration options field, select Configure
Transaction Programs, then click on the New button.
The Define a Transaction Program window opens.
- Select the Basic tab.
- Clear the the Service TP check box.
- Specify an application TP name ((8)) in the TP name
field.
- Select the Background Process check box.
- Select the Advanced tab.
- Change the default in the Receive Allocate timeout field to 0
(no timeout).
- Accept the defaults for the other fields.
- Click on OK.
|
step 7.
| Save the configuration
- Select File->Save As. The Save As window opens.
- Type in a file name, for example ny3.acg, and click on
OK.
- In the window that opens, you are asked if you want this configuration to
be the default. Click on the Yes push button.
|
step 8.
| Update the environment
IBM Personal Communications uses an environment variable called
appcllu to set the default Local LU used for APPC
communications. You may set this variable on a per-session basis by
opening a command window and typing set
appcllu=local_lu_name, where local_lu_name is the name
of the local LU you want to use. However, you will probably find it
more convenient to permanently set the variable. To permanently set the
variable in Windows NT, complete the following steps:
- Click on the Start push button and select
Settings->Control Panel.
- Double-click on the System icon. The System Properties window
opens.
- Select the Environment tab.
- Type appcllu in the Variable field.
- Type your local LU name ((4)) in the Value field.
- Click on the Set push button to accept the changes.
- Click on OK to exit the System Properties window.
The environment variable will now remain set for future sessions.
|
step 9.
| Start SNA Node Operations
- Click Start and select Programs->IBM Personal
Communications->Administrative and PD Aids->SNA Node Operations.
The Personal Communications SNA Node Operations window opens.
- From the menu bar, select Operations->Start Node.
- In the window that opens, select the configuration file you saved in the
previous step (for example, ny3.acg) and click on
OK.
|
You have now finished setting up your workstation for inbound APPC
communications.
This section describes how to configure your Microsoft
SNA Server 4.0 to accept inbound APPC client connections.
For more information on setting up your environment, refer to the online
help supplied with SNA Server, or to the following publications:
- Connectivity Supplement
- DRDA Connectivity Guide
The following assumptions have been made:
- The basic installation of the Microsoft SNA Server 4.0 for Windows
NT package has already been completed.
- DB2 Connect or DB2 Universal Database for Windows NT has been
installed.
Use the Your Values entries in the worksheet in Table 22 to complete the steps below.
| The transaction program name required for inbound APPC connections is
automatically defined for the worksation when the SNA Server is
installed. These instructions describe the remaining steps required to
configure your APPC communications for inbound connections.
|
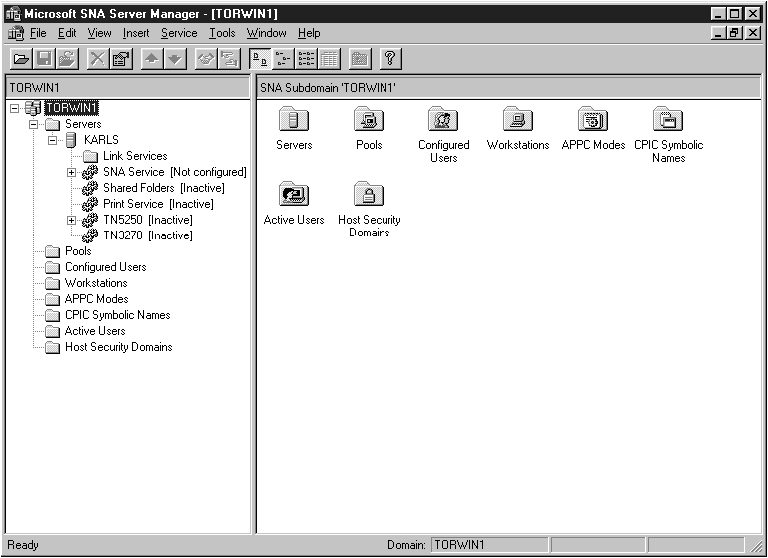
You can define the properties of your SNA connections in the Microsoft SNA
Server Manager. The Server Manager uses an interface similar to that of
the Windows NT Explorer. Figure 1 shows the interface. There are two panes in the main
window of the Manager. All the required configuration options can be
accessed by right-clicking on objects in the left-hand pane of the
window. Every object has a context menu that you can access
by right-clicking on the object.
Figure 1. The Microsoft SNA Server Manager
To configure APPC communications for inbound connections using Microsoft
SNA Server Manager, perform the following steps:
step 1.
| Start the Server Manager by clicking on the Start button and
selecting Programs->Microsoft SNA Server->Manager.
|
step 2.
| Define the control point name
- Click on the [+] sign beside the Servers
folder.
- Right-click on the SNA Service folder and select the
Properties option. The Properties window opens.
- Enter your Network ID ((1)) in the NETID field.
- Enter your local Control Point name ((2)) in the Control Point
Name field.
- Click on OK.
|
step 3.
| Define a local LU
- Right-click on the SNA Service icon and select the
Insert->APPC->Local Lu option. The Local APPC LU Properties
window opens.
- Enter the following information:
- The LU alias ((5)).
- The NETID((1)).
- The LU name ((4)).
- Select the Advanced tab.
- Select the Member of Default Outgoing Local APPC LU Pool
option. Accept the other defaults.
- Click on OK.
|
step 4.
| Define a mode
- Right-click on the APPC Modes folder, and select the
Insert->APPC->Mode Definition option. The APPC Mode
Properties window opens.
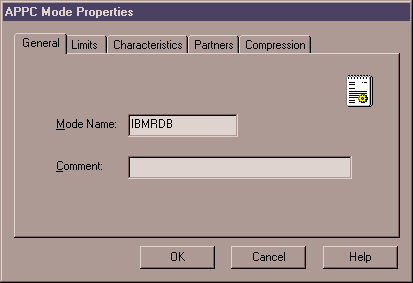
- Enter the Mode Name (6) in the Mode Name field.
- Select the Limits tab.
- Enter appropriate numbers in the Parallel Session Limit and
Minimum Contention Winner Limit fields. Your Network
administrator should be able to supply you with the numbers if you do not know
the limits you should place here.
- Accept the other defaults, and click on OK.
|
step 5.
| Save the configuration
- Select File->Save File in the Server Manager window. The
Save File window opens.
- Type a unique name for your configuration into the File Name
field.
- Click on the Save button. Your configuration is now
saved.
|
You have now finished setting up your workstation for inbound APPC
communications.
This chapter describes how to configure your Solaris
server to accept inbound APPC client connections.
Before you begin, ensure that your workstation has SunLink SNA PU
2.1 Server for Solaris installed.
For more information on setting up your environment, refer to:
- Connectivity Supplement
- DRDA Connectivity Guide
- SunLink PU 2.1 Server Configuration and Administrator's
Manual..
The following assumptions have been made:
- The basic installation of theSunLink SNA PU 2.1 Server for Solaris
package has already been completed.
- DB2 Connect or DB2 Universal Database has been installed.
- The user is logged on as root.
Use the Your Values entries in the worksheet in Table 22 to complete the steps below.
To configure the SunLink SNA PU 2.1 Server to accept inbound APPC
connections, log on as root and edit or create the Server configuration
file. This file is called sunpu2.config, and it must
be placed in /opt/SUNWpu21, or the directory where SunLink SNA PU
2.1 Server is installed. You can use any plain text editor to
create the configuration file.
The example below shows the configuration file sections required for
configuring the server to accept inbound APPC client connections. Other
sections that are not shown are required for establishing server to host
connections.
// SunLink SunLU6.2/SunPU2.1 SNA Server Sample Configuration
// Token Ring Peer-to-Peer System A @(#)sunlu62.a.tr
//
// The physical connection is a Token Ring interface adapter.
CP NAME=NYX1GW // Local name (8 char max)
NQ_CP_NAME=SPIFNET.NYX1GW // Network Qualified Name
;
TRLINE NAME=MAC1 // SunLink specific name
SOURCE_ADDRESS=x'400011527509' // sysA_mac_addr for Sun machine
;
LU NAME=NYX1GW0A // Local name (8 char max)
NQ_LU_NAME=SPIFNET.NYX1GW0A // Network Qualified Name
SESS_LMT=50 // Max LU sessions
LUTYPE=6.2
;
MODE NAME=IBMRDB // Mode Name (8 char max)
DLC_NAME=NYX2 // Associated DLC
PTNR_LU_NAME=NYX2 // Associated Local LU
LCL_MAX_SESS_LMT=30 // Max Session Limit
MIN_CW_SESS=15 // Min Conwinners
MIN_CL_SESS=15 // Min Conlosers
;
// This section adds DLC for the inbound APPC client NYX2
DLC NAME=NYX2, // User defined name (8 char max)
LINK_NAME=MAC1, // Line name this station is on
LCLLSAP=x'04', // Local Link Service Access Point
RMTLSAP=x'04', // Remove Link Service Access Point
RMTMACADDR=x'400011528901', // sysB_mac_addr
TERMID=x'05d27510', // IDNUM and IDBLK = XID
MAXDATA=4096,
ACTIVITY_TIMEOUT=0,
RETRIES=20,
REPLY_TIMEOUT=20,
RESPONSE_TIMEOUT=20,
ACTPU_SUPPRESS=yes
;
// This section defines the partner LU NYX2
PTNR_LU NAME=NYX2, // Partner LU name (8 char max)
LOC_LU_NAME=NYX1GW0A, // Associated Local LU
NQ_LU_NAME=SPIFNET.NYX2 // Network Qualified Name
SEC_ACCEPT=ALREADY_VERIFIED // Accept client as already verified
;
// This section adds the TP name NYSERVER
// and associates it with the local LU NYX1GW01
TP TP_NAME=DB2DRDA, // TP Name
LOC_LU_NAME=NYX1GW0A, // Associated Local LU
CONV_TYPE=BASIC, // Conversation Type
;
//
SECURITY LOC_LU_NAME=NYX1GW0A, // Local LU Alias
USER_ID=USERID, // User id
PASSWORD=PASSWORD, // Password (since UNIX_SEC=NO)
;
When you have finished editing and saving the server configuration file,
perform the following steps:
step 1.
| Start and stop the SunLINK subsystem
- Change to the SunLink directory, which is usually
/opt/SUNWpu21.
- Set up environment variables for FlexLM licensing. For
example:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/openwin/lib:/usr/lib
export LM_LICENSE_FILE=/etc/opt/licenses/licenses_combined
For more information, refer to the SunLink documentation.
- Ensure you have created the SNA server configuration file in the
/opt/SUNWpu21 directory.
- Use the sunop utility to check the status of SunLink SNA if it
is already started.
Check to see if the PU and/or DLC status is connected.
Refer to the SunLink documentation for details of the sunop
utility.
- Stop SunLink if it is active. For example, enter:
kill -9 sunpu2.pid
- Start SunLink using the following command:
sunpu2.1
|
step 2.
| Set the following environment variables:
APPC_GATEWAY
| Name of the DB2 for Solaris server (usually the TCP/IP hostname).
| APPC_LOCAL_LU
| Name of the local LU name provided in the SNA configuration file
((4)).
|
Export these on the server machine.
|
You have now finished setting up your workstation for inbound APPC
communications.
[ Top of Page | Previous Page | Next Page | Table of Contents | Index ]
[ DB2 List of Books |
Search the DB2 Books ]