A string is a sequence of bytes that may represent characters. Within a string, all the characters are represented by a common coding representation. In some cases, it might be necessary to convert these characters to a different coding representation. The process of conversion is known as character conversion. 12
Character conversion can occur when an SQL statement is executed remotely. Consider, for example, these two cases:
In either case, the string could have a different representation at the sending and receiving systems. Conversion can also occur during string operations on the same system.
The following list defines some of the terms used when discussing character conversion.
For example, the following character set appears in several code pages:
In the ASCII encoding scheme for code page 850, for example, 'A' is assigned code point X'41' and 'B' is assigned code point X'42'. Within a code page, each code point has only one specific meaning. A code page is an attribute of the database. When an application program connects to the database, the database manager determines the code page of the application.
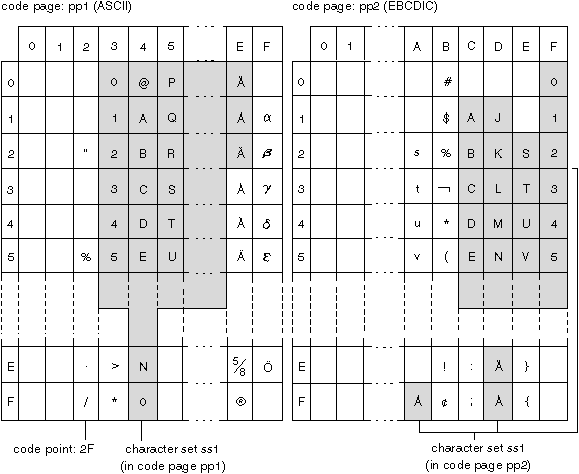
The following example shows how a typical character set might map to different code points in two different code pages.

Even with the same encoding scheme, there are many different code pages, and the same code point can represent a different character in different code pages. Furthermore, a byte in a character string does not necessarily represent a character from a single-byte character set (SBCS). Character strings are also used for mixed and bit data. Mixed data is a mixture of single-byte, double-byte, or multi-byte characters. Bit data (columns defined as FOR BIT DATA or BLOBs, or binary strings) is not associated with any character set.
The database manager determines code page attributes for all character strings when an application is bound to a database. The potential code page attributes are:
Character string code page attributes are as follows:
A set of rules is used to determine the code page attributes for operations that combine string objects, such as the results of scalar operations, concatenation, or set operations. At execution time, code page attributes are used to determine any requirements for code page conversions of strings.
For more details on character conversion, see: