Quick Beginnings for DB2 Universal Database EEE for Windows NT**
You can administer local or remote servers using the DB2
Administration Tools. Use the Control Center to perform
administration tasks such as configuring DB2 instances and databases, backing
up and recovering data, scheduling jobs, and managing media, all from a
graphical interface.
The Control Center uses TCP/IP to retrieve status, connection, and snapshot
information from each database partition server (node). You assign a
TCP/IP port number for the Performance Monitor component of the Control Center
during installation.
The Control Center for Version 6 has additional support for DB2 UDB for
OS/390.
| Note: | This option is only available on DB2 Enterprise Edition, DB2 Enterprise -
Extended Edition, DB2 Connect Personal Edition, and DB2 Connect Enterprise
Edition.
|
If you want to access DB2 for OS/390 functions from the Control
Center:
- Verify the following information with your systems administrator:
- You have a DB2 for OS/390 license (Version 5 or later).
- You are using DB2 UDB for Enterprise Edition.
- Apply a function modification identifier. Read the DB2 for OS/390
Program Directory. The program directory identifies and describes the
contents of FMIDs for each tape or cartridge.
- Apply any additional service to DB2 as described in the program
directory.
- Ensure that you enabled the stored procedures address space.
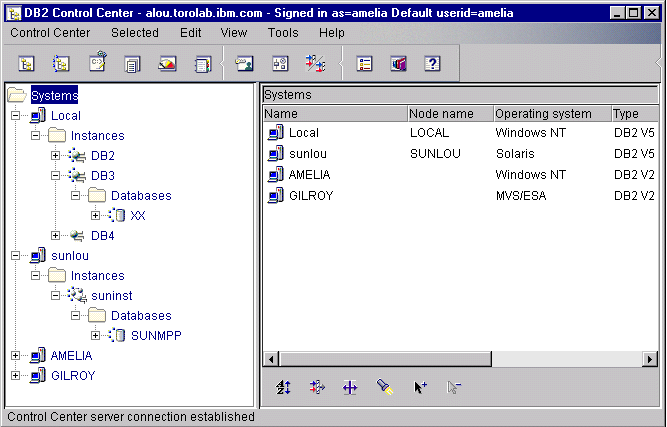
The Control Center displays instances and database objects
(such as table spaces, tables, and packages) and their relationships to each
other. Using the Control Center, you can manage local and remote
servers from a single point of control. See Figure 9 for an example of the main Control Center window.
Figure 9. Control Center Main Window
The Control Center distinguishes between single-partition and
multipartition database systems via Discovery. Discovery
uses the DB2SYSTEM, DB2ADMINSERVER, and DB2COMM
registry values. For more information on these registry values, refer
to the Administration Guide.
From the Control Center, you can perform operations on database
objects. These operations include:
- Create and drop a database
- Create, alter, and drop a table space or table
- Create, alter, and drop an index
- Create nodegroups
- Backup and recover a database partition or table space partition.
- Define the replication sources and subscriptions to replicate data between
systems
- Monitor resources and events on a server.
For more information on objects in a partitioned database system, see Introduction to DB2 Enterprise - Extended Edition.
You can also control DB2 instances by:
- Maintaining communication protocols
- Setting database manager and database configuration values that affect
performance.
SmartGuides are provided to help you perform complex tasks. For
example, a SmartGuide is available to tune the performance of your
system. See Completing Tasks with SmartGuides for descriptions of the various SmartGuides and how
to start them.
The Control Center provides additional functionality to assist you in
managing your servers:
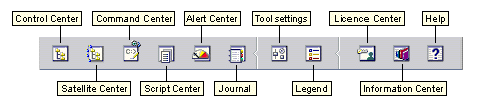
- Control Center
- Use the Control Center to start another session of the Control Center to
administer a server.
- Satellite Center
- Use the Satellite Center to manage the Satellites that are served by a
particular DB2 Control Server. It provides create, remove, modify, and
manage functions for Satellites and Groups. You can also create and
manage scripts to administer the Satellites.
- Command Center
- Use the Command Center to enter DB2 commands and SQL statements in an
interactive window and see the execution result in a result window. You
can scroll through the results and save the output to a file.
- Script Center
- Use the Script Center to create scripts, which you can store and invoke at
a later time. These scripts can contain DB2 commands, SQL statements,
as well as operating system commands. Scripts can be scheduled to run
unattended. These jobs can be run once or set up to run on a repeating
schedule; a repeating schedule is particularly useful for tasks like
backup.
- Alert Center
- Use the Alert Center to monitor your system for early warnings of
potential problems or to automate actions to correct problems
discovered.
- Journal
- Use the Journal to view all available information about jobs that are
pending execution, executing, or that have completed execution. You can
also view the recovery history log, the alerts log, and the messages log; and
review the results of jobs that are run unattended.
- Tools Setting
- Use the Tools Setting to change the settings for the DB2 Administration
Tools.
- License Center
- Use the License Center to manage licenses and display license status and
usage of any DB2 products installed on your system. You can also use
the License Center to configure your system for proper license
monitoring.
- Information Center
- The Information Center provides quick access to DB2 product
information. This product information includes such items as:
database tasks, reference material, DB2 documentation, troubleshooting aids,
sample programs for application development, and DB2 web-related URLs.
You can also analyze performance using the DB2 Performance Monitor and
Visual Explain. These tools are available from the Control
Center.

| Use the DB2 Performance Monitor to monitor the performance of
your system. You can monitor activity by sampling data over a period of
time or using data for a particular event. See "Monitoring Databases Using DB2 Performance Monitor" for more information.
|
| Use Visual Explain to view the access plan for explained SQL
statements as a graph. You can use the information available from the
graph to tune your SQL queries for better performance. See "Viewing SQL Access Plans Using Visual Explain" for more information.
|
You can find additional information in the Administration Guide or in the online help.
The Control Center allows you to maintain or edit server
protocol settings in the database manager configuration file.
- Configure communication parameters in the database manager by clicking
with the right mouse button on an instance and selecting the
Configure option from the pop-up menu.
| By default, the setup program automatically detects and configures most
communication protocols that it detects on your system.
|
- Export database information in a profile that can be used to configure
clients by clicking with the right mouse button on a system and selecting the
Export option from the pop-up menu.
| DB2 Personal Edition does not accept inbound client requests for
data. You can only configure inbound communications on a DB2 Personal
Edition workstation to allow administrative requests from a DB2 Administration
Client.
|
For information on how to configure server communications, refer to the
Installation and Configuration Supplement.
With the DB2 Performance Monitor, you can:
- Identify and analyze performance problems in database applications or the
database manager.
- Use the early warning system to detect potential problems.
- Automate actions to correct problems that are discovered.
- Define your own statistics, in addition to the default set that is
provided.
You can choose to monitor the current state of database activity or collect
information when specific events occur. The Performance Monitor allows
you to capture point-in-time information at specified intervals. The
Event Analyzer allows you to view information about the occurrence of events
such as deadlocks and transaction completions.
For additional information, refer to the Administration
Guide or the online help.
|
You are also able to use the Windows NT Performance Monitor to monitor both
database and system performance. For information on how to register DB2
resources and to use the Windows NT Performance Monitor, refer to the Administration Guide.
|
Visual Explain helps database administrators and
application developers to:
- View the access plan chosen by the database manager's optimizer for a
given SQL statement.
- Tune SQL statements for better performance.
- Design application programs and databases.
- View all the details of an access plan, including the statistics in the
system catalogs.
- Decide whether or not to add an index to a table.
- Identify the source of problems by analyzing the access plan or
performance of SQL statements.
- Use the portable snapshot function to view snapshots from any remote DB2
server.
- Display access plans for queries on all supported DB2
configurations.
For additional information, refer to the Administration
Guide or the online help.
[ Top of Page | Previous Page | Next Page | Table of Contents | Index ]
[ DB2 List of Books |
Search the DB2 Books ]