
The PREPARE statement is used by application programs to dynamically prepare an SQL statement for execution. The PREPARE statement creates an executable SQL statement, called a prepared statement, from a character string form of the statement, called a statement string.
Invocation
This statement can be embedded only in an application program. It is an executable statement that cannot be dynamically prepared.
Authorization
For statements where authorization checking is performed at statement preparation time (DML), the privileges held by the authorization ID of the statement must include those required to execute the SQL statement specified by the PREPARE statement. For statements where authorization checking is performed at statement execution (DDL, GRANT, and REVOKE statements), no authorization is required to use the statement; however, the authorization is checked when the prepared statement is executed.
Syntax
>>-PREPARE--statement-name----+------------------------+-------->
'-INTO--descriptor-name--'
>----FROM--host-variable---------------------------------------><
Description
The statement string must not:
There are two types of parameter markers:
CAST(? AS data-type)
This notation is not a function call, but a "promise" that the type of the parameter at run time will be of the data type specified or some data type that can be converted to the specified data type. For example, in:
UPDATE EMPLOYEE
SET LASTNAME = TRANSLATE(CAST(? AS VARCHAR(12)))
WHERE EMPNO = ?
the value of the argument of the TRANSLATE function will be provided at run time. The data type of that value will either be VARCHAR(12), or some type that can be converted to VARCHAR(12).
Typed parameter markers can be used in dynamic SQL statements wherever a host variable is supported and the data type is based on the promise made in the CAST function.
Untyped parameters markers can be used in dynamic SQL statements in
selected locations where host variables are supported. These locations
and the resulting data type are found in Table 25. The locations are grouped in this table into
expressions, predicates and functions to assist in determining applicability
of an untyped parameter marker. When an untyped parameter marker is
used in a function (including arithmetic operators, CONCAT and datetime
operators) with an unqualified function name, the qualifier is set to
'SYSIBM' for the purposes of function resolution.
Table 25. Untyped Parameter Marker Usage
| Untyped Parameter Marker Location | Data Type |
|---|---|
| Expressions (including select list, CASE and VALUES) | |
| Alone in a select list | Error |
| Both operands of a single arithmetic operator, after considering operator
precedence and order of operation rules.
Includes cases such as: ? + ? + 10 | Error |
| One operand of a single operator in an arithmetic expression (not a
datetime expression)
Includes cases such as: ? + ? * 10 | The data type of the other operand. |
| Labelled duration within a datetime expression. (Note that the portion of a labelled duration that indicates the type of units cannot be a parameter marker.) | DECIMAL(15,0) |
| Any other operand of a datetime expression (for instance 'timecol + ?' or '? - datecol'). | Error |
| Both operands of a CONCAT operator | Error |
| One operand of a CONCAT operator where the other operand is a non-CLOB character data type | If one operand is either CHAR(n) or VARCHAR(n), where n is less than 128, then other is VARCHAR(254 - n). In all other cases the data type is VARCHAR(254). |
| One operand of a CONCAT operator where the other operand is a non-DBCLOB graphic data type. | If one operand is either GRAPHIC(n) or VARGRAPHIC(n), where n is less than 64, then other is VARCHAR(127 - n). In all other cases the data type is VARCHAR(127). |
| One operand of a CONCAT operator where the other operand is a large object string. | Same as that of the other operand. |
| As a value on the right hand side of a SET clause of an UPDATE statement. | The data type of the column. If the column is defined as a user-defined distinct type, then it is the source data type of the user-defined distinct type. |
| The expression following CASE in a simple CASE expression | Error |
| At least one of the result-expressions in a CASE expression (both Simple and Searched) with the rest of the result-expressions either untyped parameter marker or NULL. | Error |
| Any or all expressions following WHEN in a simple CASE expression. | Result of applying the Rules for Result Data Types to the expression following CASE and the expressions following WHEN that are not untyped parameter markers. |
| A result-expression in a CASE expression (both Simple and Searched) where at least one result-expression is not NULL and not an untyped parameter marker. | Result of applying the "Rules for Result Data Types" to all result-expressions that are other than NULL or untyped parameter markers. |
| Alone as a column-expression in a single-row VALUES clause that is not within an INSERT statement. | Error |
| Alone as a column-expression in a multi-row VALUES clause that is not within an INSERT statement, and for which the column-expressions in the same position in all other row-expressions are untyped parameter markers. | Error |
| Alone as a column-expression in a multi-row VALUES clause that is not within an INSERT statement, and for which the expression in the same position of at least one other row-expression is not an untyped parameter marker or NULL. | Result of applying the Rules for Result Data Types on all operands that are other than untyped parameter markers. |
| Alone as a column-expression in a single-row VALUES clause within an INSERT statement. | The data type of the column. If the column is defined as a user-defined distinct type, then it is the source data type of the user-defined distinct type. |
| Alone as a column-expression in a multi-row VALUES clause within an INSERT statement. | The data type of the column. If the column is defined as a user-defined distinct type, then it is the source data type of the user-defined distinct type. |
| As a value on the right side of a SET special register statement | The data type of the special register. |
| Predicates | |
| Both operands of a comparison operator | Error |
| One operand of a comparison operator where the other operand other than an untyped parameter marker. | The data type of the other operand |
| All operands of a BETWEEN predicate | Error |
Either
operands of a BETWEEN predicate | Same as that of the only non-parameter marker. |
| Remaining BETWEEN situations (i.e. one untyped parameter marker only) | Result of applying the Rules for Result Data Types on all operands that are other than untyped parameter markers. |
| All operands of an IN predicate | Error |
| Both the 1st and 2nd operands of an IN predicate. | Result of applying the "Rules for Result Data Types" on all operands of the IN list (operands to the right of IN keyword) that are other than untyped parameter markers. |
| The 1st operand of an IN predicate where the right hand side is a fullselect. | Data type of the selected column |
| Any or all operands of the IN list of the IN predicate | Data type of the 1st operand (left hand side) |
| The 1st operand and zero or more operands in the IN list excluding the 1st operand of the IN list | Result of applying the "Rules for Result Data Types" on all operands of the IN list (operands to the right of IN keyword) that are other than untyped parameter markers. |
| All three operands of the LIKE predicate. | Match expression (operand 1) and pattern expression (operand 2) are VARCHAR(32672). Escape expression (operand 3) is VARCHAR(2). |
| The match expression of the LIKE predicate when either the pattern expression or the escape expression is other than an untyped parameter marker. | Either VARCHAR(32672) or VARGRAPHIC(16336) depending on the data type of the first operand that is not an untyped parameter marker. |
| The pattern expression of the LIKE predicate when either the match expression or the escape expression is other than an untyped parameter marker. | Either VARCHAR(32672) or VARGRAPHIC(16336) depending on the data type of the first operand that is not an untyped parameter marker. If the data type of the match expression is BLOB, the data type of the pattern expression is assumed to be BLOB(32672). |
| The escape expression of the LIKE predicate when either the match expression or the pattern expression is other than an untyped parameter marker. | Either VARCHAR(2) or VARGRAPHIC(1) depending on the data type of the first operand that is not an untyped parameter marker. If the data type of the match expression or pattern expression is BLOB, the data type of the escape expression is assumed to be BLOB(1). |
| Operand of the NULL predicate | error |
| Functions | |
| All operands of COALESCE (also called VALUE) or NULLIF | Error |
| .Any operand of COALESCE where at least one operand is other than an untyped parameter marker. | Result of applying the Rules for Result Data Types on all operands that are other than untyped parameter markers. |
| An operand of NULLIF where the other operand is other than an untyped parameter marker. | The data type of the other operand |
| POSSTR (both operands) | Both operands are VARCHAR(32672). |
| POSSTR (one operand where the other operand is a character data type). | VARCHAR(32672). |
| POSSTR (one operand where the other operand is a graphic data type). | VARGRAPHIC(16336). |
| POSSTR (the search-string operand when the other operand is a BLOB). | BLOB(32672). |
| SUBSTR (1st operand) | VARCHAR(32672) |
| SUBSTR (2nd and 3rd operands) | INTEGER |
| The 1st operand of the TRANSLATE scalar function. | Error |
| The 2nd and 3rd operands of the TRANSLATE scalar function. | VARCHAR(32672) if the first operand is a character type. VARGRAPHIC(16336) if the first operand is a graphic type. |
| The 4th operand of the TRANSLATE scalar function. | VARCHAR(1) if the first operand is a character type. VARGRAPHIC(1) if the first operand is a graphic type. |
| The 2nd operand of the TIMESTAMP scalar function. | TIME |
| Unary minus | DOUBLE PRECISION |
| Unary plus | DOUBLE PRECISION |
| All other operands of all other scalar functions including user-defined functions. | Error |
| Operand of a column function | Error |
Notes
Examples
Example 1: Prepare and execute a non-select-statement in a COBOL program. Assume the statement is contained in a host variable HOLDER and that the program will place a statement string into the host variable based on some instructions from the user. The statement to be prepared does not have any parameter markers.
EXEC SQL PREPARE STMT_NAME FROM :HOLDER END-EXEC. EXEC SQL EXECUTE STMT_NAME END-EXEC.
Example 2: Prepare and execute a non-select-statement as in example 1, except code it for a C program. Also assume the statement to be prepared can contain any number of parameter markers.
EXEC SQL PREPARE STMT_NAME FROM :holder; EXEC SQL EXECUTE STMT_NAME USING DESCRIPTOR :insert_da;
Assume that the following statement is to be prepared:
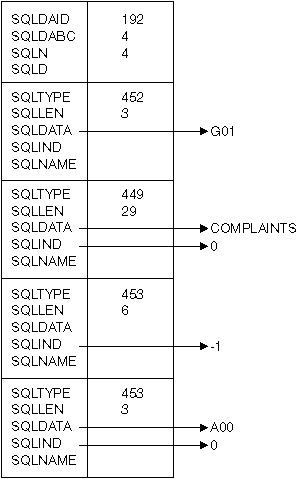
INSERT INTO DEPT VALUES(?, ?, ?, ?)
The columns in the DEPT table are defined as follows:
DEPT_NO CHAR(3) NOT NULL, -- department number DEPTNAME VARCHAR(29), -- department name MGRNO CHAR(6), -- manager number ADMRDEPT CHAR(3) -- admin department number

To insert department number G01 named COMPLAINTS, which has no manager and reports to department A00, the structure INSERT_DA should have the above values before issuing the EXECUTE statement.