
Administering Satellites Guide and Reference
This section describes the process of migrating an
existing system to DB2 Satellite Edition from previous releases. The
following releases are supported for Version 6 migration: DB2 Common
Server Version 2.x, Database Server Version 4.x, and DB2
Universal Database Version 5.x.
| Note: | The migration process for Database Server Version 4 is identical to that used
for DB2 Common Server Version 2. Whenever Version 2 is mentioned in
this section, the same information also applies to Version 4.
|
DB2 migration involves the following procedures:
These steps will help you to ensure that all databases
on your system can be migrated to the new DB2 Version 6 format. Before
installing your new version of DB2, perform the following steps:
You should back up all databases before installing
your new version of DB2. To back up the databases, perform the
following steps:
- Complete all database transactions.
- Ensure all applications disconnect from each database.
To list all applications that are connected to a database, enter the
db2 list applications command. If all applications are
disconnected, this command will return the following message:
SQL1611W No data was returned by the Database System Monitor. SQLSTATE=00000
To force all applications to disconnect from the database, enter the
db2 force applications all command.
- Ensure all databases are cataloged. To view a list of all the
cataloged databases in the current instance, enter the following
command:
db2 list database directory
- Make a backup copy of all databases. For more information on
backing up databases, refer to the Administration
Guide for the DB2 version you are backing up. For the syntax of the
backup command, refer to the Command Reference for the DB2 version you are backing up.
| Note: | Make sure that this is the most recent backup copy of the database before you
start the next procedure.
|
- Stop the database manager by entering the db2stop
command.
DB2 provides the db2ckmig command to check
that databases can be migrated. This command must be run prior to
installation. The command is located on the product CD-ROM.
To run the db2ckmig command:
- Insert the CD-ROM into the drive.
| Note: | If you are installing DB2 on a Windows 9x or Windows NT workstation, the
setup program might be started automatically using the operating system's
auto-run feature. In this case, do not proceed with the install.
Instead, cancel and proceed to the next step.
|
- Enter the db2ckmig command to verify that the databases on your
system can be migrated. The syntax of the command is as follows:
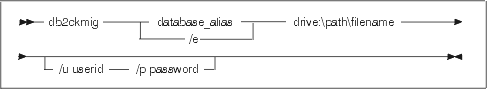
- database_alias
- Specifies a database_alias name of a database to be verified for
migration. This parameter is required if the /e parameter is
not specified.
- /e
- Specifies that all cataloged databases are to be verified for
migration. This parameter is required if the database_alias
parameter is not specified.
- /l drive:\path\filename
- Specifies a drive, target path and filename to keep a list of errors and
warnings generated for the scanned database. The path variable
is optional; if you do not specify a path, the path from which you
execute the db2ckmig command will be used. There is no
default when installing from the CD-ROM. You must specify a
filename.
- /u userid
- Specifies the user account used to connect to the database. This
parameter must be specified if the /p parameter is
specified.
- /p password
- Specifies the password of the user account used to connect to the
database. This parameter must be specified if the /u
parameter is specified.
For example, to check that all databases cataloged on your system can be
migrated and to log all the messages from this command to the
c:\temp\message.txt file, enter the following command:
x:\db2\common\db2ckmig /e /l c:\temp\message.txt
where x: represents your CD-ROM drive.
- If any errors are found, the db2ckmig command generates a log
file and places it in the path and file specified by the /l
option. When the errors are corrected, enter the db2ckmig
command again to ensure that the databases are ready to be migrated.
Table 4.
Correcting Error Messages
| Error
| Action
|
| A database is in backup pending state
| Perform a backup of the database.
|
| A database is in roll-forward pending state
| Recover the database as required. Perform or resume a roll-forward
database to end of logs and stop.
|
| Table space ID is not in normal state
| Recover the database and table space as required. Perform or
resume a roll-forward database to end of logs and stop.
|
| A database is in an inconsistent state
| Restart the database to return it to a consistent state.
|
| The Version 2 database contains database objects that have a schema name
of SYSCAT, SYSSTAT, or SYSFUN
| These schema names are reserved for the Version 6 database
manager.
To correct this error, perform the following steps:
- Back up the database.
- Export the data from the database object (catalogs or tables).
- Drop the object.
- Re-create the object with another schema name.
- Import/Load the data into the object.
- Run the db2ckmig command against the database again, ensuring
that the database passes the db2ckmig check.
- Make a backup copy of the database.
For more information, refer to the Administration
Guide.
|
The Version 2 database contains database objects that have a dependency
on the SYSFUN.DIFFERENCE function. Possible violated database
objects are:
- Constraint
- Function
- Trigger
- View
| The SYSFUN.DIFFERENCE function must be dropped and re-created
during database migration. However, if there is a database object that
is dependent on this function, migration will fail.
To correct this error:
- Constraint
- Enter the alter table command to drop the constraint.
- Function
- Enter the drop function command to drop the function dependent
on SYSFUN.DIFFERENCE.
- Trigger
- Enter the drop trigger command to drop the trigger.
- View
- Enter the drop view command to drop the view.
| Note: | Any package dependent on the SYSFUN.DIFFERENCE function will be marked
inoperative after migration. As a result, the db2ckmig
command will not report any package that is dependent on the
SYSFUN.DIFFERENCE function.
|
For more information, refer to the Administration
Guide.
|
| The database contains user-defined distinct types (UDTs) that use the
type name BIGINT, DATALINK, REAL or REFERENCE.
| These data type names are reserved for the Version 6 database
manager.
To correct this error, perform the following steps:
- Back up the database.
- Export the data from any tables that are dependent on the data
types.
- Drop any tables dependent on the data types, and then drop the data
types. These drops may drop other objects such as views, indexes,
triggers, or functions.
- Create data types with different type names and re-create the tables using
the new data type names. Re-create any dropped views, indexes,
triggers, or functions.
- Import/Load the data into the object.
- Run the db2ckmig command against the database again, ensuring
that the database passes the db2ckmig check.
- Make a backup copy of the database.
For more information, refer to the Administration
Guide.
|
| Structured type and function have the same name.
| A structured type and function (with no arguments) belonging to the same
schema cannot have the same name. The type or function and objects
using the type or function have to dropped and re-created using another
name.
To correct this error, perform the following steps:
- Back up the database.
- Export the data from any tables that are dependent on the structured types
or functions.
- Drop any tables dependent on the structured types or functions, and then
drop the structured types or functions. These drops may drop other
objects such as views, indexes, triggers, or functions.
- Create structured types or functions with different type or function names
and re-create the tables using the new data type or function names.
Re-create any dropped views, indexes, triggers, or functions.
- Import/Load the data into the object.
- Run the db2ckmig command against the database again, ensuring
that the database passes the db2ckmig check.
- Make a backup copy of the database.
For more information, refer to the Administration
Guide.
|
| Note: | These instructions apply only to the DB2 Version
2.x db2uexit user exit program. If you are not using
the Version 2.x db2uexit user exit program, skip this
section and continue at Installing DB2 Satellite Edition Version 6.
|
DB2 Version 6 uses the db2uexit user exit program to archive and
retrieve log files. For more information on the db2uexit
interfaces, refer to the Administration Guide.
The following should be considered before migrating from Version 2.x
to Version 6.
- If the Version 2.x user exit program,
db2uexit.exe, located in the \sqllib\bin directory before
installation, it will remain in this directory after the installation
completes. The db2uext2.exe program will also be
installed in this directory. Its function is to invoke the
db2uexit.cmd or db2uexit.exe user exit
programs using the Version 2.x interface. This allows the old
user exit program to be used on Version 6.
- If db2uexit.exe is in a directory other than the
sqllib\bin directory, it will remain there after installation, but
db2uext2.exe will not be installed in the sqllib\bin
directory. Following installation, if you want to use the old user exit
program, you will have to copy it to the sqllib\bin directory, then copy
db2uext2.v2 from the sqllib\misc directory to the sqllib\bin
directory, and rename it to db2uext2.exe.
If you are migrating from DB2 Version 2.x, you should modify your
user exit program to use the DB2 Version 6 interfaces. The new user
exit program db2uexit should replace db2uext2 in the
sqllib\bin directory.
After you have successfully completed the
pre-installation checks, you can now start installing DB2 Satellite Edition
Version 6 using either the interactive or distributed method as described in Interactive Installation or Distributed Installation. During the installation of DB2 Satellite Edition
Version 6, instance migration for instances created in previous versions of
DB2 occurs.
After installing DB2 Version 6, you can now migrate
databases and complete other migration activities. Do not make any
changes to the database system before migrating all the databases;
otherwise, the database migration will fail.
To migrate pre-Version 6 databases owned by an
instance, perform the following steps:
- Log in with a user account that has SYSADM authority.
- Ensure that the databases you want to migrate are cataloged. To
retrieve a list of all catalogued databases on your system, enter the db2
list database directory command.
- Migrate the database using the db2 migrate database
command. For more information, refer to the Command
Reference.
After database migration is complete, you can perform
the following post-migration activities:
- Migrate Unique Indexes
- Update Statistics
- Rebind Packages
- Update Database and Database Manager Configuration
- Migrate Explain Tables
You can also apply these activities to a back-level database backup that
is restored to Version 6, since at the end of the restore the database is
migrated to Version 6.
- Migrate Unique Indexes (db2uiddl)
- DB2 Versions 5 and 6 support deferred checking for duplicate index key
values until the end of UPDATE statements. This ensures that temporary
duplicate index key values which may be present in mid-UPDATE, but
no longer are present at the end of the UPDATE, will not cause the statement
to fail.
| Note: | You must install the Client Tools sub-component of the Miscellaneous Tools to
use the db2uiddl command. Client Tools component can only be
installed during a custom install.
|
With DB2 Version 2 the same UPDATE statement may fail because checking for
duplicate key index values is performed row by row as the statement processes
the table. For example, if a row with value 1 is changed to value 2,
but a row with value 2 already exists, a duplicate value 2 will be detected
causing the DB2 Version 2 UPDATE statement to fail.
| Note: | Version 2.x and 5.x unique indexes are not automatically
migrated to Version 6 semantics for the following reasons:
- Converting unique indexes is a time-consuming operation.
- You may have applications that depend on the previous version's
unique index semantics.
- You may want to manage the staged conversion of unique indexes on your own
schedule, when needed, using the db2uiddl command.
All existing applications will continue to work even if the unique indexes
are not converted to Version 6 semantics. You have to convert unique
indexes to Version 6 semantics only if support for deferred uniqueness
checking is required.
|
To convert unique indexes, you need to perform the following steps:
- Log in with a user account that has SYSADM authority.
- Start the database manager by entering the db2start
command.
- Run the db2uiddl command against your migrated database.
Refer to the Command Reference for the syntax of this command.
The db2uiddl command searches the database catalog tables and
generates all the CREATE UNIQUE INDEX statements for user tables in an output
file.
- Review the output generated from the db2uiddl command.
You should remove any unwanted indexes from the output file to reduce the time
needed to execute it. Comments in the output will flag other situations
that require your attention.
- Connect to the database by entering the db2 connect to
database_alias command, where database_alias is the
alias of the database you are migrating.
- Execute the output file, generated by the db2uiddl command, as
a DB2 CLP command file, using a command similar to the following:
db2 -tvf filename
where filename represents the file generated by the
db2uiddl command.
| Note: | DB2 interprets the re-creation of an existing unique index using the
db2uiddl command to signal that the index is ready to be converted
to Version 6 semantics.
|
- Disconnect from the database by entering the db2 connect reset
command.
- Update Statistics
- When database migration is completed, the old statistics that are used to
optimize query performance are retained in the catalogs. However,
Version 6 of DB2 has statistics that are modified or do not exist in Versions
2.x or 5.x. To uses these statistics for better
application performance, you may want to execute the runstats
command on tables, particularly those tables that are critical to the
performance of your SQL queries.
Refer to the Command Reference for the syntax of the runstats command. For details on the
statistics, refer to the Administration Guide.
- Rebind Packages
-
During database migration, all existing packages are invalidated.
After the migration process, each package is rebuilt when it is used for the
first time by the Version 6 database manager.
For better performance, you should run the db2rbind command to
rebuild all packages stored in the database. In DB2 Version 6 this
command has a new option, all, which, when specified, rebinds all
packages (valid and invalid). If the all option is not
specified with the db2rbind command, only those packages marked as
invalid are rebound. Refer to the Command
Reference for the syntax of this command.
- Update Database and Database Manager Configuration
- Some of the database configuration parameters are changed to Version 6
defaults or to other values during database migration. The same is true
for database manager configuration parameters which may have changed to
Version 6 defaults or to other values. For more information about
configuration parameters, refer to the Administration
Guide.
| Note: | You should run the DB2 Performance Monitor for suggestions in choosing
appropriate configuration parameters. For more information about using
the DB2 Performance Monitor, refer to System Monitor Guide
and Reference.
|
- Migrate Explain Tables
- To migrate the explain tables in a database that has been migrated to
Version 6, run the following command:
db2exmig -d dbname -e explain_schema [-u userid password]
where:
- dbname represents the database name. This parameter is
required.
- explain_schema represents the schema name of the explain tables
to be migrated. This parameter is required.
- userid and password represent the current user's ID
and password. These parameters are optional.
| Note: | You must install the Database Tools sub-component of the Miscellaneous Tools
to use the db2exmig command. Database Tools component can
only be installed during a custom installation.
|
The explain tables belonging to the user ID that is running
db2exmig, or that is used to connect to the database, will be
migrated. The explain tables migration tool will rename the Version 2
or Version 5 tables, create a new set of tables, using the
EXPLAIN.DDL, and copy the contents of the old tables to the
new tables. Finally, it will drop the old tables. The migration
utility, db2exmig, will preserve any user added columns on the
explain tables.
[ Top of Page | Previous Page | Next Page | Table of Contents | Index ]
[ Top of Page ]

