Administering Satellites Guide and Reference
The satellites of a particular group need to be in a state consistent with
the other satellites of its group. The consistent state can be
accomplished with synchronization.
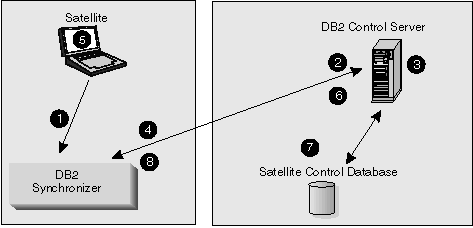
Figure 2 provides a high-level view of how a satellite
synchronizes. Before the satellite can synchronize, it must connect to
the network on which the DB2 control server resides. The satellite can
connect with the network in a variety of ways, such as by a dial-up program,
by docking with the network, or by remaining permanently connected to the
network.
Figure 2. Satellite Synchronization
The satellite synchronizes as follows:
- The end-user of the satellite invokes the synchronizer function.
The invocation can be from your user application (if it calls the
db2SyncSatellite API), or from the DB2 Synchronizer application that is
provided with DB2. For information about the APIs that an application
can call for synchronization, see Synchronizing a Satellite. Also refer to the Administrative
API Reference. For information about the DB2 Synchronizer, see Using the DB2 Synchronizer Application.
When the synchronizer function is invoked, steps 2 through 8 occur automatically. No manual
intervention is required.
The satellite is only connected to the satellite control database for step 3, and for step 7.
- The satellite connects to the satellite control database, where
it is authenticated.
- After authentication occurs, the DB2 control server checks
which group the satellite belongs to, and the version of the application that
the satellite is executing. The DB2 control server uses this
information to determine which batches the satellite should execute, and which
batch steps should be executed, if any. At this time, other events may
also occur:
- If the satellite could not upload the results of its previous
synchronization session to the satellite control database, the results are
written at this time.
- If any of the scripts in a batch to be downloaded are
parameterized, the DB2 control server instantiates the script with the values
that are appropriate for the satellite. For more information about
parameterized scripts, see Parameterizing Scripts.
- When steps 3a and 3b are complete (if required), the DB2 control
server releases the scripts that the satellite is to execute, and the
satellite downloads them. When this occurs, the tables in the satellite
control database are updated to indicate that the satellite has obtained the
batches that apply to it.
- The synchronizer function drops the connection with the satellite control
database.
- The satellite executes the batches that it downloaded.
- After executing the batches, the synchronizer function again
connects to the satellite control database.
- The synchronizer function updates the log information in the
satellite control database with the results of the execution of the different
steps of the batches. The log information provides details about the
execution of the batch steps. For information about these logs, refer
to the online help that is available from the Satellite Administration
Center.
- The synchronizer function drops the connection with the
satellite control database.
After the synchronization session is complete, the satellite can be
disconnected from the network, if required.
[ Top of Page | Previous Page | Next Page | Table of Contents | Index ]
[ Top of Page ]