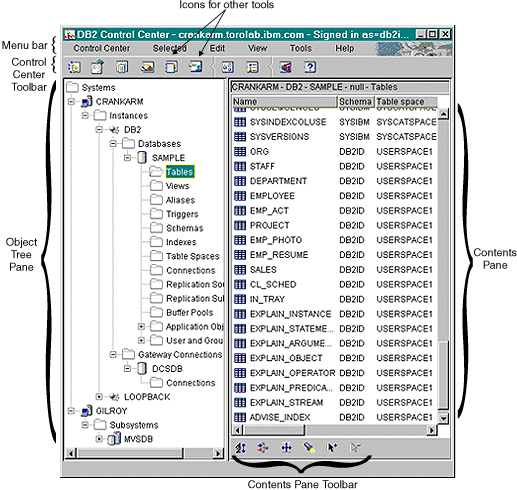

Use the Control Center as your main point of administration to manage systems, DB2 instances, databases, database objects, such as tables, views, and user groups. You can also use the Control Center to access DB2 for OS/390 subsystems. All DB2 databases must be catalogued before they appear in the Control Center. The Figure 21 shows the primary features of the Control Center. Because of operating system differences, the Control Center on your system may appear different from the diagram.
Figure 21. Control Center Features
 |
The main elements of the Control Center are:
You can change the settings for these tools by selecting the Tools Settings icon from the Control Center toolbar.
Use the Customized Control Center on the DB2 for OS/390 platform as your own defined point of administration to manage subsystems, databases, or database objects, such as tables, views, and database users. You can use this Customized Control Center to access any DB2 for OS/390 objects that you define.
The main elements of the Customized Control Center are the same as those listed for the default Control Center. The Customized Control Center allows you to specify objects that you want to include in a personalized Control Center. This user-defined tree can be saved and invoked to administer DB2 objects. It does not replace the Control Center tree which is the default for all users but is useful if you want to access a set of objects in the same way each time the Control Center is invoked. You can create as many customized trees as you need, and each one can contain a different set of objects, which can be ordered in any way that you choose.
Using a customized tree reduces the effort of navigating through a fixed hierarchy of DB2 objects, and provides a method of grouping related objects. For example, you can define a tree that contains only tables with payroll information.
The Object Tree in the Control Center shows all the systems that are cataloged on the instance to which you are currently attached. If you attach to another instance, the Control Center shows the systems that are cataloged on that new instance. From the Control Center, you can administer database objects for the Universal Database family of products for OS/2, Windows, and UNIX platforms.
You can also administer DB2 for OS/390 subsystems from the Control Center if an Administration Server (DAS) is running on the DB2 for OS/390 system and if a DB2 Connect product is available to the client on which the Control Center is running. This requires either DB2 Connect Personal Edition to be installed on the client or DB2 Connect Enterprise Edition to be installed on a LAN and be accessible to the client. In addition to having a DB2 Connect product installed, a connection must be defined on the DB2 for OS/390 subsystem so that it can used by the Control Center.
From the Control Center, you can also replicate data between the DB2 Universal Database family of products, DB2 for AS/400, DB2 for VSE and VM systems, and DB2 for OS/390.
If you want to administer objects from the Control Center, you must add them to the object tree. If you remove a database, or uncatalog it outside of the Control Center, and you want to use the Control Center to perform tasks on it, you must add it to the object tree.
The DB2 Universal Database objects that you can administer from the Control Center are:
The DB2 for OS/390 Version 5 objects that you can administer from the Control Center are:
For Version 6 of DB2 UDB for OS/390, the following objects were added:
To see what actions can be performed on each of these objects, select the object in the Object pane and click mouse button 2. A pop-up window appears listing the functions.
To display all of the systems that are cataloged on your system and which have DB2 installed:
On OS/2, Windows and supported DB2 UNIX-based systems, you can think of each copy of the database manager code as a separate instance, that is stored in a directory on your machine. On DB2 for OS/390, an instance is referred to as a subsystem. A default local instance is created when you install DB2. You can have several instances on a single system. You can use these instances to separate the development environment from the production environment, or to restrict sensitive information to a particular group of people. You can also tune an instance for a particular environment.
Using the Control Center, you can perform many of the functions of the existing DB2 for OS/390 Version 5 and DB2 UDB for OS/390 Version 6 products, such as creating, altering, and dropping objects, as well as run utilities that reorganize or load your data. However, before you can administer a DB2 for OS/390 subsystem from the Control Center, you must first add it to the object tree by configuring a connection to it.
If you have the Client Configuration Assistant installed, you can use it to configure a connection to a DB2 for OS/390 subsystem easily. If you do not have the Client Configuration Assistant installed, you will have to configure the connection to the DB2 for OS/390 subsystem manually.
You use the Client Configuration Assistant to search the network for all the DB2 for OS/390 subsystems which are available on the LAN to your client. If you would like to add one of the DB2 for OS/390 subsystems, you can use the Add Database SmartGuide to add the subsystem, or you can import a connection by using an access profile, or you can add the connection manually.
If you choose to search the network, you need to have a DB2 Connect product on your network with a connection defined for the subsystem. If you choose to use an access profile, you need to import a profile for the subsystem you want to add. If you need to manually configure the connection, you need to know the subsystem name, the communication protocol, and the communication protocol parameters such as the host name and the port number for TCP/IP, or the Symbolic Destination Name for SNA. Once you add the DB2 for OS/390 subsystem, you also get the objects for the gateway connections.
When you add a DB2 for OS/390 subsystem, it appears in its own section of the Control Center object tree separate from the DB2 Universal database objects. To see the DB2 for OS/390 V5 and DB2 UDB for V6 objects that reside in a particular subsystem, expand the object tree from the DB2 for OS/390 system icon that represents your DB2 for OS/390 system.
To see the list of actions that you can perform on a particular object, select the object as it appears in the object tree and click mouse button 2. A pop-up menu appears and shows the available actions you can perform on that object. For example, you can create, alter, or drop a view, as well as see its contents, modify the privileges on it, and show a list of other objects that are related to it. See the online help for the DB2 for OS/390 objects for more information on what functions you can perform.
When a DB2 Connect server is installed, a Gateway Connections folder is displayed in the Control Center object tree under the instance object of the local system. The Gateway Connections folder contains a hierarchy of objects used to manage connections to host and AS/400 databases that are cataloged locally. The actions associated with these connection management objects can be used to list, force, and monitor host and AS/400 database connections.
The object tree under the Gateway Connections folder is used for managing connections to host and AS/400 databases but not for database administration tasks. However, if you need to add, change or remove a host or AS/400 database on the local system, you would use the Client Configuration Assistant and not the Gateway Connections tree.
From the Control Center, you can:
To see all the actions that you can perform on an object, simply select the object from the Object Tree pane or the Contents pane and click mouse button 2. A pop-up menu appears showing all the functions that you can perform on that type of object; for example, if you select the tables folder, you can create a new table with or without the help of a SmartGuide; monitor the performance of tables; filter which tables appear in the Contents pane and so on. The functions you can perform are different, depending on the object you select.
Click mouse button 2 on the objects in the Contents pane to perform additional functions on a specific object. For example, if you select one of your tables in the Contents pane and click mouse button 2, a pop-up window displays functions you can use on that table.
To create new objects:
When you click an object such as the table folder in the Object Tree pane, all tables already existing appear in the Contents pane. You can then select a table you want to work with and click mouse button 2 to invoke any functions that you wish to perform on that specific table.
For more information about using the Control Center, go to its online help, available from its Help menu or by pressing F1 anywhere in the Control Center.
You can search for a database or subsystem object easily by using the Locate notebook. This allows you to:
Use the Locate page of the Locate notebook to specify the search criteria. Use the Advanced page of the Locate notebook to further customize the search. Edit the text provided on the Advanced page and add or modify the search criteria.
To locate an object defined within a database or a DB2 for OS/390 subsystem: